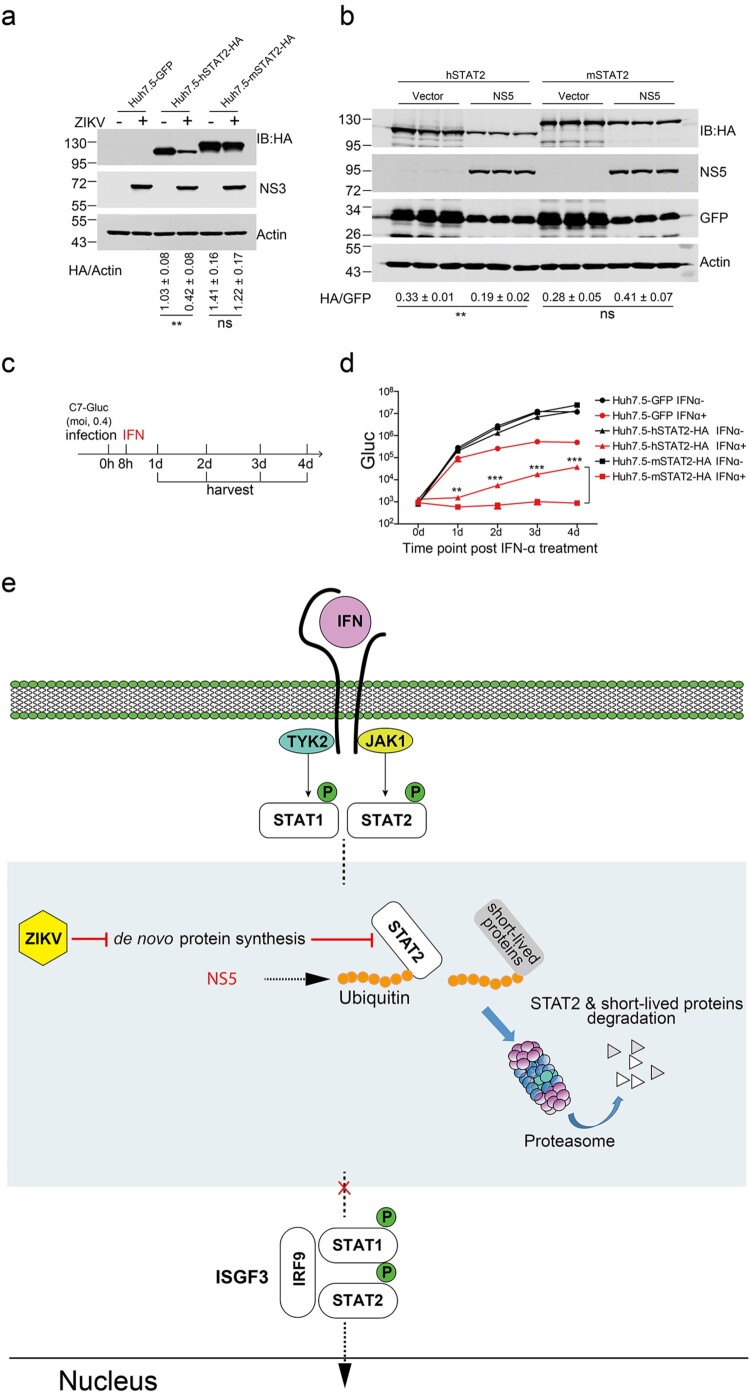
Figure 7.
Murine STAT2, which was refractory to ZIKV-induced ablation, elicited robust antiviral signalling upon IFN treatment. (a) Murine STAT2 was refractory to ZIKV-induced reduction. Huh7.5 cells stably expressing GFP, hSTAT2-HA and murine STAT2-HA (mSTAT2-HA) were infected with ZIKV (MOI = 5) for 2 d and then harvested for western blotting analysis with the indicated antibodies. Representative pictures of three biological replicates are shown. The values to the left of the blots are molecular sizes in kilodaltons. Statistical analysis was performed between the C7-infected group and NS5-expressing group and the uninfected groups (Mock) (ns, not significant, **P < 0.01; two-tailed, unpaired t-test). (b) Murine STAT2 was refractory to ZIKV NS5 induced reduction. The plasmids expressing the ZIKV Ubi-NS5 or Vector were co-transfected with hSTAT2-HA or murine STAT2-HA (mSTAT2-HA)-expressing plasmid and GFP-expressing plasmid (6:3:1) in to Vero cells for 48 h, and then harvested for western blotting analysis with the indicated antibodies. Representative pictures of three biological replicates are shown. The values to the left of the blots are molecular sizes in kilodaltons. Statistical analysis was performed between the indicated groups (ns, not significant, **P < 0.01; two-tailed, unpaired t-test). (c) Experimental design for C. Huh7.5-GFP, Huh7.5-hSTAT2-HA and Huh7.5-mSTAT2-HA cells were infected with C7-Gluc (MOI = 0.4) for 8 h and then treated with IFN-α (2000 U/ml). At the indicated time points after IFN-α treatment, cells were harvested. (d) Gluc activities in the cell lysates of Huh7.5-GFP, Huh7.5-hSTAT2-HA and Huh7.5-mSTAT2-HA cells were determined. The mean ± SD of three biological replicates is shown (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed between the indicated groups at each time point (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; two-tailed, unpaired t-test). (e) Type I interferon (IFN) binds to interferon receptors, activating the Janus kinases Jak1 and Tyk2 to engage STAT1 and STAT1 and phosphorylate STAT1 and STAT2. Phosphorylated STAT1 and STAT2 form a heterodimer and recruit IFN regulatory factor 9 (IRF-9) to assemble interferon-stimulating gene factor 3 (ISGF3). ISGF3 enters the nucleus to elicit the expression of interferon-stimulating genes. ZIKV infection interrupts host de novo protein synthesis, accelerating the degradation of the pool of ubiquitinated short-lived proteins and STAT2. As reported, NS5 may contribute to this process by facilitating NS5 ubiquitination. See details in the text.