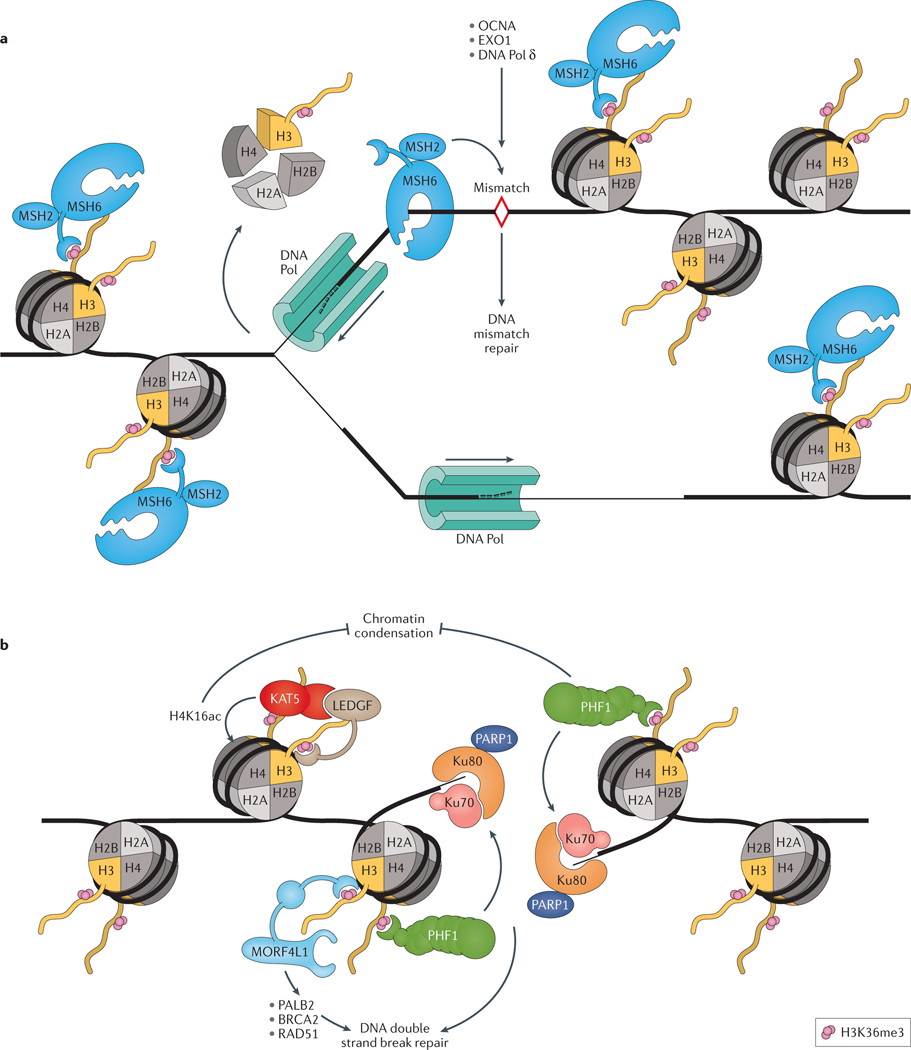
Figure 3 |. H3K36me3 facilitates DNA damage repair.
a | During DNA replication, misincorporated nucleotides and insertion–deletion mispairs are repaired through DNA mismatch repair (MMR). These replication errors can be recognized by the MutSα complexes (composed of a MSH2-MSH6 heterodimer), which can initiate MMR by recruiting proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), exonuclease 1 (EXO1) and DNA polymerase δ (DNA Pol δ) to sites of DNA damage. MutSα is recruited to genomic regions decorated with trimethylated histone H3 lysine 36 (H3K36me3), via the PWWP domain of MutS protein homolog 6 (MSH6). This nuance guarantees that MutSα is present and enriched for in coding sequences prior to DNA replication and ensures that MMR is concentrated at these regions. b | H3K36me3 also has a role in the repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs). When DSBs occur, H3K36me3 marks on nearby nucleosomes becomes exposed, leading to the recruitment of PHD finger protein 1 (PHF1) to the DSB site, where it locally recruits X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 6 (Ku70)–X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5 (Ku80) complexes and PARP1 to promote the initiation of DSB repair. Mortality factor 4-like protein 1 (MORF4L1; also known as MRG15) also participates in DSB repair by recruiting partner and localizer of BRCA2 (PALB2), which then recruits breast cancer type 2 susceptibility protein (BRCA2) and DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 (RAD51) to DSB sites. Maintaining an open chromatin state creates a favourable environment conducive to the resolution of DSBs. PHF1 also facilitates DSB repair by inhibiting the activity of factors involved in chromatin condensation, promoting a more relaxed, open chromatin state. Following DNA DSBs, MORF4L1 recruits lens epithelium-derived growth factor (LEDGF; also known as PSIP1), which subsequently recruits KAT5, a histone H4 lysine 16 (H4K16ac) acetyltransferase, and increases H4K16ac, which prevents chromatin condensation.