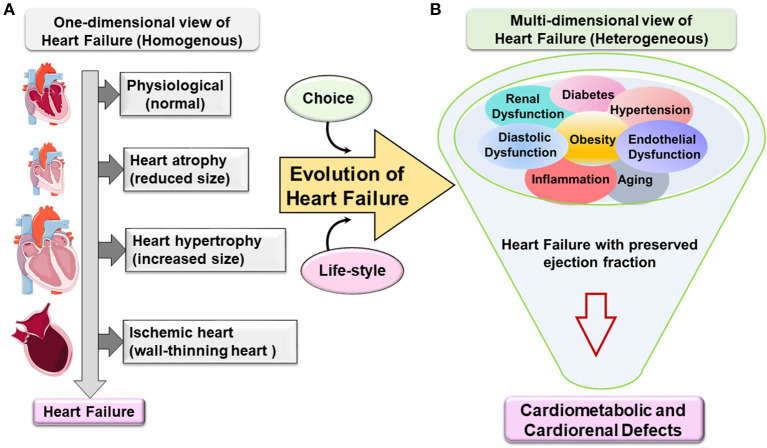
Figure 1.
Evolution of one-dimensional to multidimensional view of cardiovascular disease and heart failure. (A) One-dimensional view of heart failure (HF). Classically, HF emerges in a homogenous population based on geometry, structure, and function. The progress from being a phenotypically normal to abnormal structure accompanied with a decrease or increase in the (cardiomyocyte) heart size due to eccentric or concentric remodeling or following ischemic injury with dilation of the chambers and wall-thinning effect. HF specifically with preserved ejection fraction evolves from one-dimensional view to multidimensional view. (B) Metabolic defects directed the multidimensional view of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Heterogeneous metabolic comorbidities are a primary confounder in HFpEF patients like obesity, hypertension, kidney dysfunction, diabetes, aging, etc. The complexity of the HFpEF syndrome resulted in cardiometabolic and cardiorenal defects with signs of suboptimal inflammation without any current treatment.