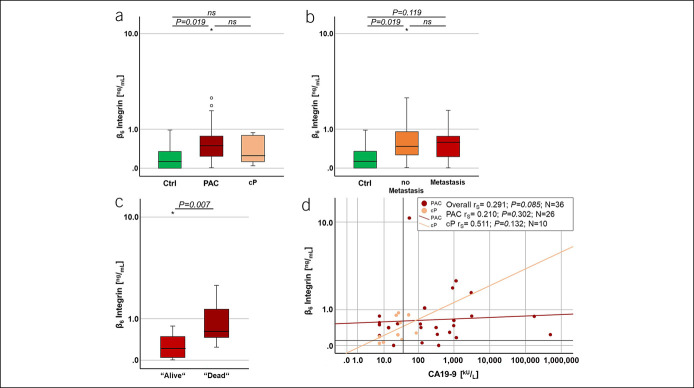
Figure 1.
Validation of ITGB6 as possible biomarker for PAC. (a) Serum ITGB6 levels were assessed in a prospective study cohort of 27 patients with PAC (cohort 1, N = 27). As control served 9 healthy volunteers (Ctrl; N = 9) and 10 patients with cP (N = 10). Significant differences in ITGB6 levels were observed between patients with PAC and Ctrl (P = 0.019). (b) Comparing patients with or without distant metastatic PAC, serum ITGB6 levels were not significantly different. However, a significant increase in ITGB6 levels was observed between Ctrl and patients with nonmetastatic PAC (P = 0.019). (c) To assess the prognostic value of serum ITGB6 levels, patients with PAC were plotted against their status of survival at time of blood assessment. A significant difference in ITGB6 concentration was observed between patients with PAC with status alive vs dead (P = 0.007). (d) Two-dimensional scatterplots depict serum ITGB6 levels in relation to the serum CA19-9 levels from each cP (rs = 0.511; P = 0.132) and patient with PAC (rs = 0.210; P = 0.302). In (a–c), Mann–Whitney U Exact and Sig. 2-Tailed test were performed, and in (d), Spearman's rho correlation (rs) and Sig. 2-tailed test were performed. (d) Red lines indicate ITGB6 cutoff value at 0.1 ng/mL and black line CA19-9 cutoff value at 37.0 kU/L, respectively. cP, chronic pancreatitis; Ctrl, control; ITGB6, β6-integrin; PAC, pancreatic adenocarcinoma; rs, Spearman's rho correlation. *Means P < 0.05.