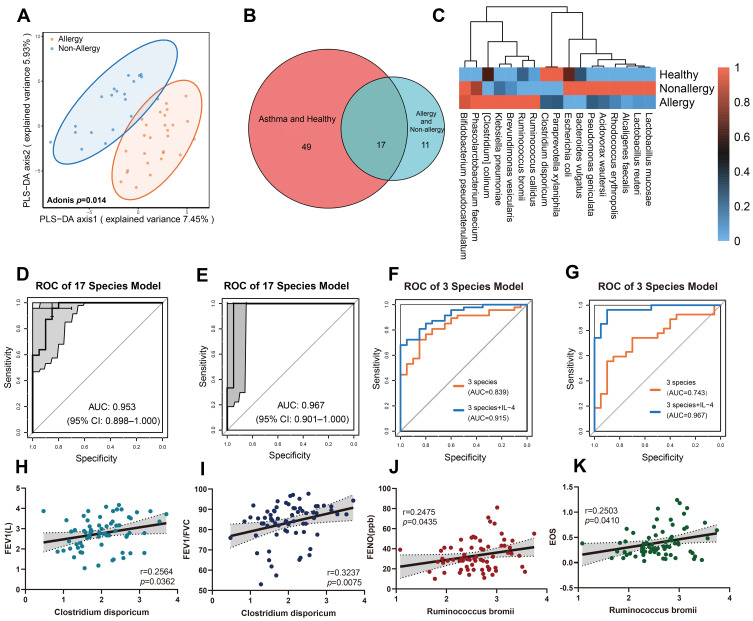
Figure 2.
Differences of intestinal microbiome between different asthma endotypes. (A) PLS-DA of intestinal microbiome difference between allergic and non-allergic asthmatic patients (Adonis, p = 0.014). (B and C) Differential species of gut microbiome in allergic, non-allergic asthmatic patients, and healthy controls. (D and E) The AUC of 17 differential species reached 0.953 to predict asthma from healthy controls (D), and 0.967 to distinguish allergic/non-allergic cohort (E). (F and G) Combination of Ruminococcus bromii, Brevundimonas vesicularis and Clostridium disporicum resulted in an AUC of 0.839 to discriminate healthy/asthma cohort (F) and 0.743 in allergic/non-allergic cohort (G). (H and I) Clostridium disporicum was positively correlated with FEV1 (r = 0.2564, p = 0.0362) (H) and FEV1/FVC ratio (r = 0.3237, p = 0.0075), (I). (J and K) Ruminococcus bromii was positively correlated with FENO (r = 0.2475, p = 0.0435) (J) and EOS level (r = 0.2503, p = 0.041) (K).