FIG 4.
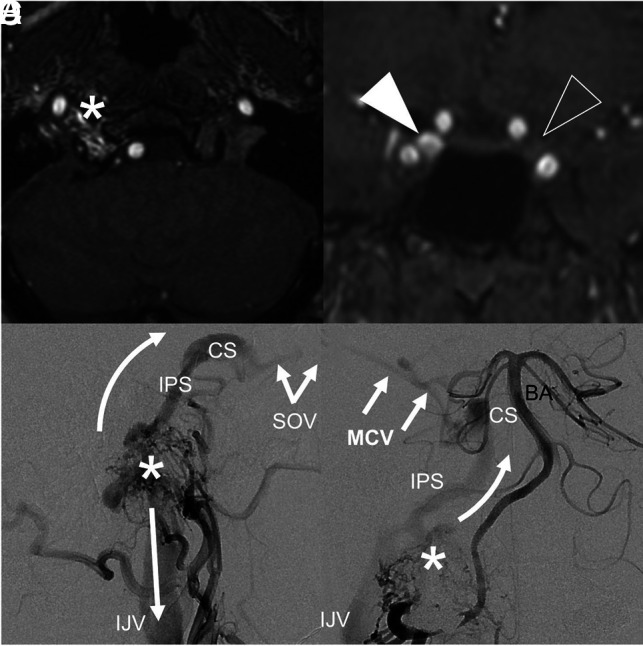
A type 3 FMR-AVF with clinical features mimicking a carotid cavernous fistula. MRA of the FMR (A) shows flow-related enhancement in the right hypoglossal canal, corresponding to an anterior condylar vein fistula site. Coronal MRA (B) shows asymmetric flow-related enhancement of the right (white arrowhead) relative to left (clear arrowhead) cavernous sinuses. Lateral-projection DSA of the right ascending pharyngeal artery (C) shows the fistula (asterisk) with antegrade drainage via the IJV (straight arrow) and reflux via the inferior petrosal sinus (IPS, curved arrow) extending to the cavernous sinus (CS) and superior ophthalmic vein (SOV), resulting in proptosis and chemosis. Anterior-posterior DSA of the right vertebral artery (D) shows reflux via the IPS and CS, which continues to the middle cerebral vein (MCV), making this a high-risk type 3 fistula. The asterisk represents the fistulous shunt site. BA indicates the basilar artery.
