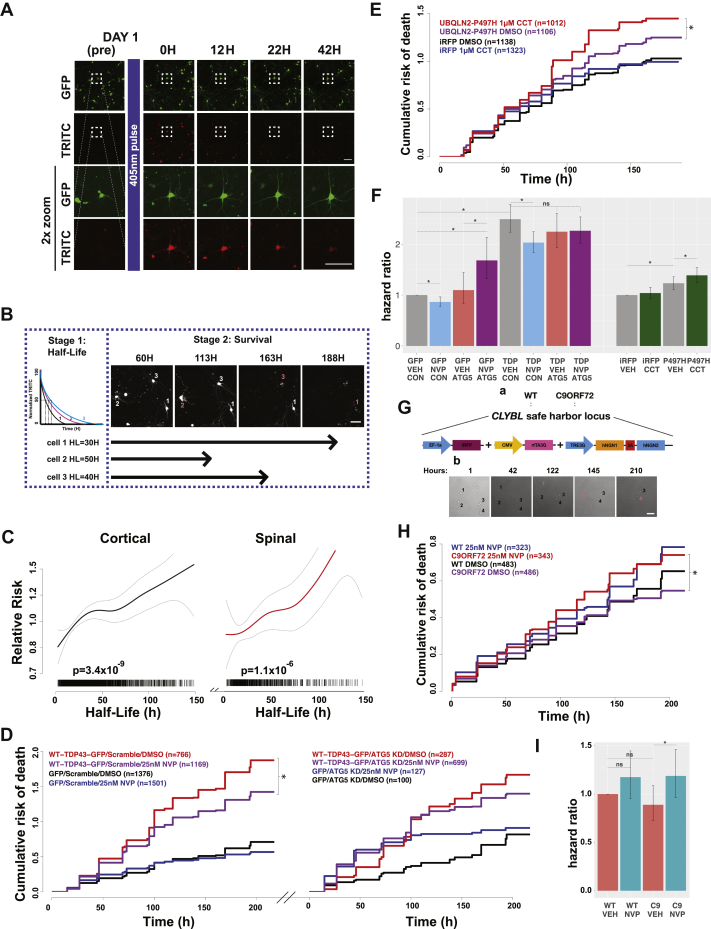
Figure 7.
Autophagy modulation has distinct effects in ALS/FTD disease models.A, mixed rodent spinal neurons were transfected on DIV 4 with Dendra2-LC3, imaged 24h later (Day 1 pre), then pulsed with 405 nm light to photoconvert Dendra2-LC3 before imaging repeatedly and longitudinally over several days to track the time-dependent loss of red fluorescence and neuronal survival. Scale bars = 100 μm in each panel. B, experimental outline for determining the relationship between Dendra2-LC3 half-life and neuronal survival. After calculating Dendra2-LC3 half-life for individual neurons (Stage 1), each cell is prospectively tracked using automated microscopy to determine its time of death (Stage 2; red number and corresponding arrow). Scale bar = 100 μm. C, penalized spline Cox proportional hazards model depicting Dendra2-LC3 half-life (x-axis) versus relative risk of death (y-axis) for primary cortical (black) and spinal (red) neurons, demonstrating a strong proportional relationship for both populations (cortical: p = 3.4 × 10−9; spinal p = 1.1 × 10−6, linear Cox proportional hazards). Each hash mark represents an individual neuron, collected from three biological and eight technical replicates each. Gray dotted lines mark 95% confidence intervals. D, NVP-BEZ235 (25 nM NVP) treatment suppresses toxicity in primary cortical neurons cotransfected with WT-TDP43-GFP and scramble siRNA, but not those transfected with WT-TDP43-GFP and ATG5 siRNA. Table S2 summarizes the hazard ratio and statistical significance of each comparison as determined by Cox proportional hazards analysis. N for each group represents total neurons pooled from three biological replicates. ∗p < 0.05, Cox proportional hazards analysis. E, CCT128930 (1 μM) treatment increased toxicity in primary cortical neurons overexpressing iRFP-P497H-UBQLN2. Table S3 summarizes hazard ratio and statistical significance of each comparison. F, hazard ratios calculated in D and E. ∗p < 0.05, Cox proportional hazards analysis. Error bars mark 95% confidence intervals. G, a, schematic depicting the generation of WT and mutant C9ORF72 iPSC-derived neurons. b, day 14 neurons were treated with the indicated compound, imaged for an additional 10 days, and time of death recorded for each neuron (red numbers). Scale bar = 100 μm. H, NVP-BEZ235 (25 nM NVP) treatment increased toxicity in mutant C9ORF72 neurons, but not WT controls. Table S5 summarizes the hazard ratios and statistical significance. N for each group represents total neurons pooled from three replicate experiments. ∗p < 0.05, Cox proportional hazards analysis. I, hazard ratios from the experiments in (H). Error bars denote 95% confidence intervals.