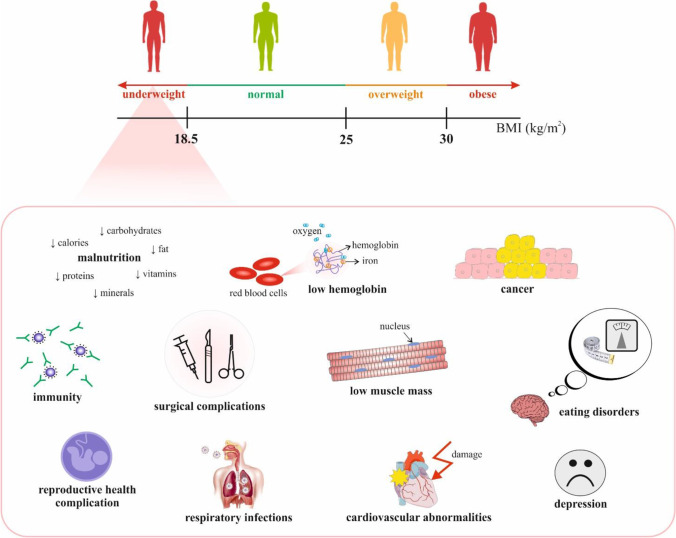
Fig. 3.
Health risks potentially associated with low body weight; Explanatory notes: BMI classification: underweight—BMI < 18.5 kg/m2; normal weight—BMI = 18.5 to 25 kg/m2; overweight—BMI ≥ 25 to < 30 kg/m2; obese—BMI ≥ 30 to < 35 kg/m2; and severely obese—BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2 [40, 41]. Selected suggested mechanisms behind increased risk of specific health complication associated with underweight include the following: abnormal nutritional status, low body fat (e.g. anorexia athletica) or low muscle mass, muscular atrophy [42], cardiovascular abnormalities, valvular dysfunction, compromised immunity [43]; cancer—particularly poor outcomes of some cancers, potentially decreased tolerability/effectiveness of cancer treatment e.g. due to lower haemoglobin and albumin resulting from abnormal nutritional status, cachexia, impaired anti-tumour immunity [44], loss of muscle fat mass, sarcopenia [45], increased risk of several cancer types and metastatic disease [6, 46, 47]; impaired healing and increased post-surgical complications—abnormal nutritional status, insufficient energy supply, shifted metabolic pathways and microbiome alterations [4, 24, 48], potentially low preoperative haemoglobin [49, 50]; reproductive dysfunction—disruption of hypothalamic-pituitary–gonadal axis leading to hypothalamic anovulation [51], ovulatory dysfunction [52], negative effects on IVF parameters [53–55]; compromised immunity—abnormal nutritional status, lymphopenia [56]; respiratory infections including COVID-19—malnutrition [57], coexisting chronic conditions [58], immuno-suppression as a result of malnutrition [59]; eating disorders (anorexia nervosa)—negative effects on overall and reproductive health [60]; neurological disorders such as young stroke [12] and abnormal pain sensitivity / perception [4, 7]; abnormal sleep patterns [7, 11, 15] and depression [61]; primary vascular dysregulation—abnormal nutrition, low energy supply, Flammer syndrome, high Endothelin-1 level in blood plasma, increased stress sensitivity, amongst others [4, 9, 15, 17, 62]; Sicca syndrome with severe complications [11, 13, 15].