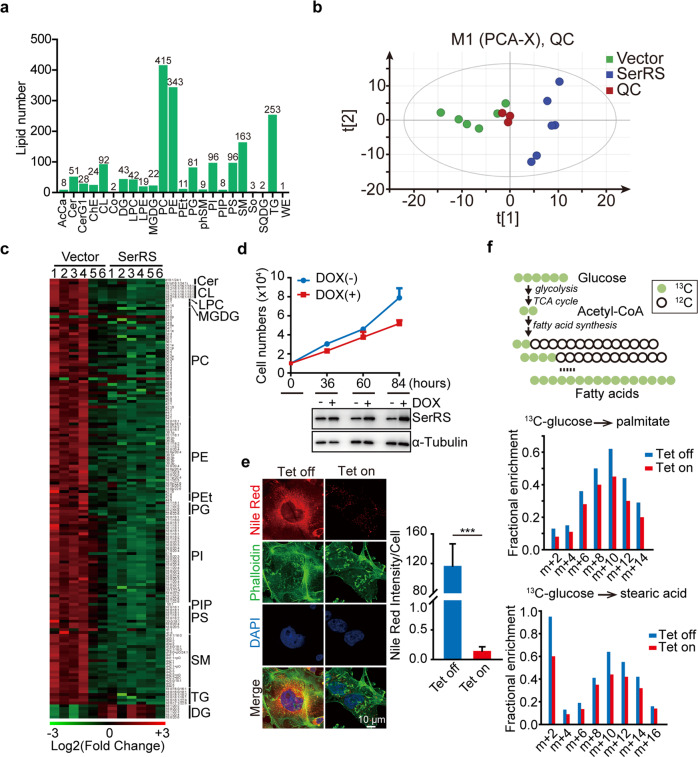
Fig. 5.
SerRS inhibits the de novo lipid synthesis in breast cancer cells. a The lipid species identified in the metabolomics analysis of MDA-MB-231 cells stably transfected with empty vector or SerRS. AcCa acyl carnitines; Cer ceramides; CerG1 glucosylceramides; ChE cholesteryl esters; CL cardiolipins; Co coenzyme; DG diradylglycerolipids; LPC lysophosphatidylcholines; LPE lysophosphatidylethanolamines; MGDG monogalactosyldiacylglycerols; PC phosphatidylcholines; PE phosphatidylethanolamines; PEt phosphatidylethanols; PG phosphatidylglycerols; phSM phytosphingosines; PI phosphatidylinositols; PIP phosphatidylinositol phosphates; PS phosphatidylserines; SM sphingomyelins; So sphingosines; SQDG sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerols; TG triradylglycerolipids; WE wax esters. b Principal component analysis (PCA) of lipids identified in MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with empty vector or SerRS (n = 6). QC quality control. c Heatmap of lipid species with significant changes (p < 0.05, n = 6) in SerRS- overexpressed versus control MDA-MB-231 cells. d Cell proliferation curves of MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with Tet-inducible SerRS which was induced by 1 mg/ml of doxycycline (DOX). The SerRS expression was monitored by western blot (low panel). e The lipid droplets (LDs) in MDA-MB-231 cells with Tet-induced SerRS were shown by immunofluorescent staining using Nile red (red). Actin filaments were counterstained with phalloidin (green). The LDs were quantified by measuring the intensity of red fluorescent signals (means ± SEM, n = 6, Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.0001). f Metabolic flux analysis of SerRS-inducible MDA-MB-231 cells labeled by 13C-glucose that is utilized for the de novo fatty acid synthesis (upper panel). The incorporation of 13C into palmitate and stearic acid in SerRS-induced (Tet on) and uninduced MDA-MB-231 cells were shown in the low panels