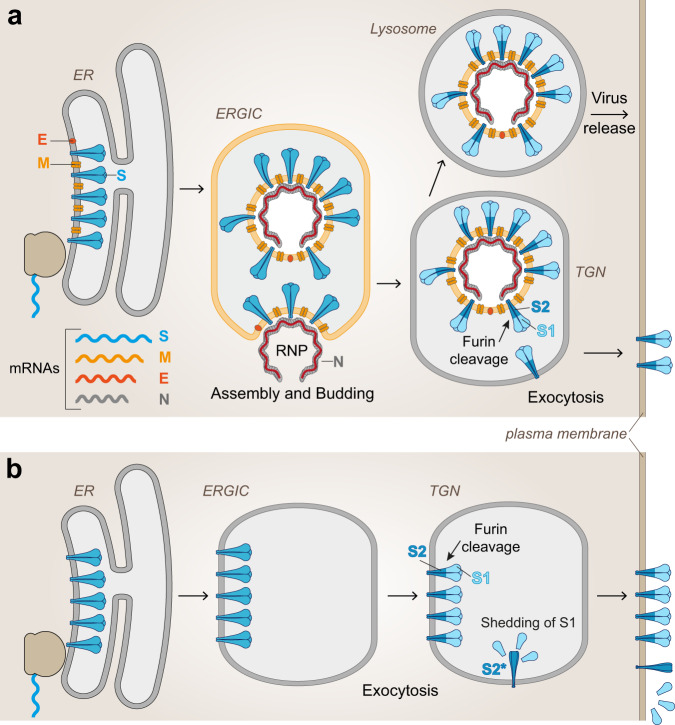
Fig. 1. Biosynthesis and intracellular transport of S.
a Infected cells: Subgenomic mRNAs for viral structural proteins are translated in association with the ER (S, M, and E) or in the cytoplasm (N), and virus assembly takes place in the ERGIC. Virus particles are transported through the TGN and released from the cells probably via lysosomes. During transport, S is cleaved into S1 and S2 by the cellular protease furin in the TGN. Some spike molecules, not assembled into virions, are also transported to the plasma membrane despite the presence of an ER retention signal15. b Transfected cells: Biosynthesis of S occurs in the absence of interactions with other viral proteins. Proteolytic cleavage into S1 and S2 occurs in the TGN similar to that in infected cells, but some shedding of cleaved S1 and conversion of S2 into its post-fusion structure (S2*) may occur in the absence of stabilizing mutations. ER—endoplasmic reticulum; ERGIC—endoplasmic reticulum Golgi intermediate compartment; TGN—Trans Golgi Network; RNP—Ribonucleoprotein; Viral proteins: S—spike, M—membrane; E—envelope; N—nucleoprotein.