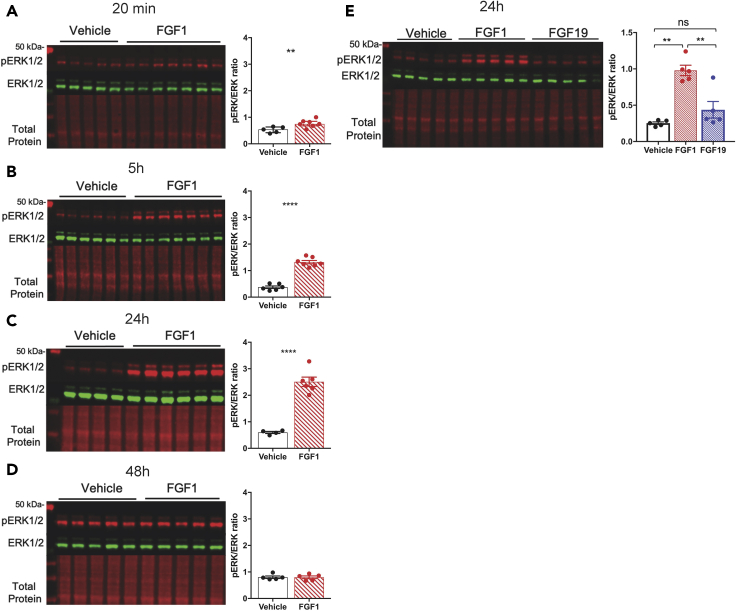
Figure 1.
Central administration of FGF1 induces sustained ERK1/2 signaling in the MBH
(A–D) Representative western blot (left) and quantitative comparison (right) of phosphorylated (red) and total ERK1/2 (green) and total protein (red) from mediobasal hypothalamic punches from adult male C57Bl6J mice after a single icv injection of either vehicle or FGF1 (3 μg) at (A) 20 min (n = 5 icv Veh, n = 7 icv FGF1, t = 3.2497 df = 9.8554 p = 0.00444), (B) 5 hours (n = 6 icv Veh, n = 7 icv FGF1, t = 11.937 df = 10.624 p = 8.62 × 10−8), (C) 24 hours (n = 4 icv Veh, n = 6 icv FGF1, t = 10.528, df = 5.4845, p = 3.816 × 10−5), and (D) 48 hours (n = 5 icv Veh, n = 5 icv FGF1, t = −0.0344, df = 7.8827, p = 0.5133) after injection. pERK1/2 ratio unpaired Welch two sample t test (one sided). ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001.
(E) Quantitative western blot of ERK1/2 phosphorylation 24 h after a single icv injection of vehicle, FGF1, or FGF19 (n = 5 icv Veh, n = 5 icv FGF1, n = 5 icv FGF19, one-way ANOVA F(2,3.46) = 54.83 p = 0.00241).
Data are represented as mean ± SEM.