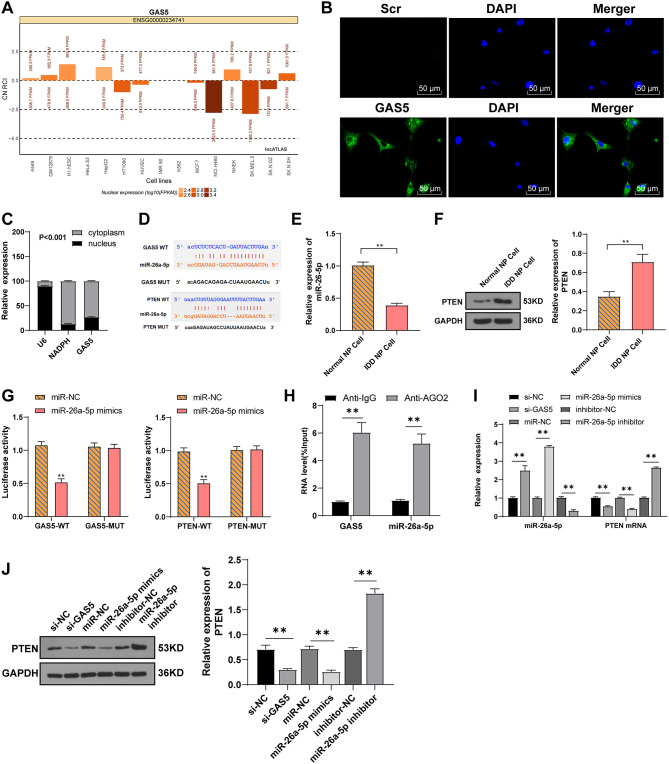
Figure 3.
LncRNA GAS5 and PTEN competitively bind to miR-26a-5p. (A) LncATLAS predicted that lncRNA GAS5 was mostly located in the cytoplasm. (B) FISH assay and (C) nuclear-cytoplasmic RNA separation confirmed the distribution of lncRNA GAS5 in degenerative NPCs. (D) Starbase and TargetScan predicted the binding sites between lncRNA GAS5 and miR-26a-5p, and miR-26a-5p and PTEN. (E) RT-qPCR was used to detect miR-26a-5p expression. (F) Western blot was used to detect PTEN expression. (G) Dual-luciferase assay confirmed the binding relation between lncRNA GAS5 and miR-26a-5p, and miR-26a-5p, and PTEN. (H) RIP test verified the interaction between lncRNA GAS5 and miR-26a-5p. (I) RT-qPCR was used to detect the miR-26a-5p expression and PTEN mRNA expression in degenerative NPCs. (J) Western blot was used to detect PTEN expression in degenerative NPCs. The cell experiment was repeated three times, and the data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation; independent t-test was used for comparison between two groups in (E–H), while one-way ANOVA was used for comparison among multiple groups in (I,J), followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test. **p < 0.01.