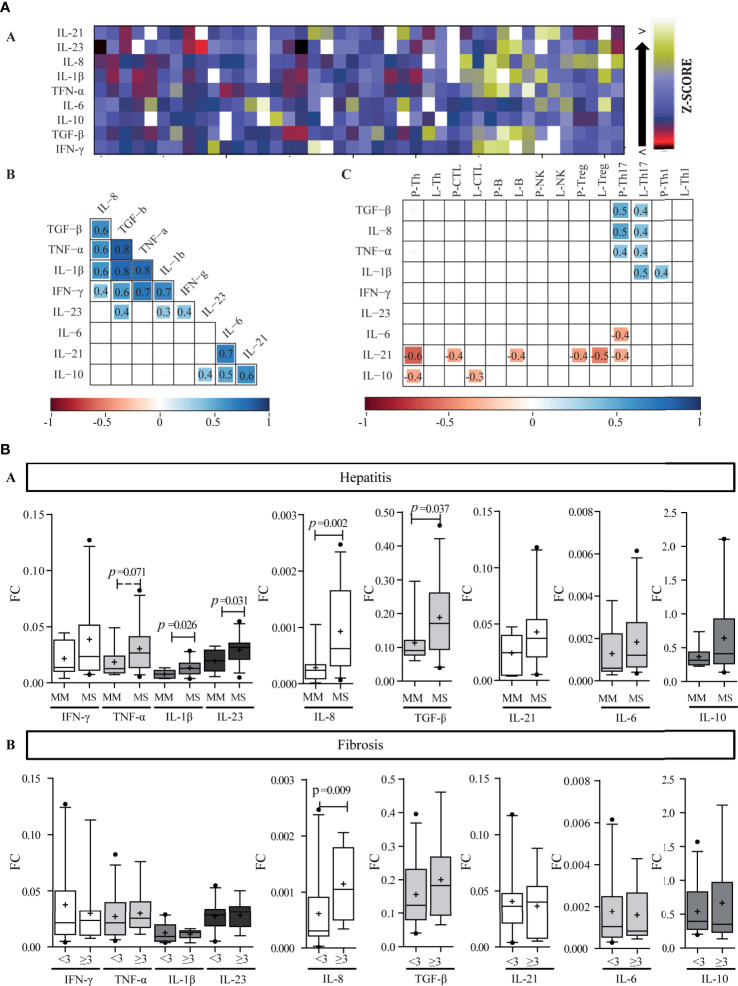
Figure 4.
Liver cytokine expression level. (A) Heat map of liver cytokine expression level (a). Each row corresponds to the cytokine indicated at the top, and each column represents one case. The data are normalized, and the results are expressed as a Z-score (Xi-/SD), which is assigned a color scale that goes from black (lowest values) to yellow (highest values). The white boxes correspond to the cases without data. Correlation matrix of cytokines (b) and correlation matrix between infiltrate cell populations and intrahepatic cytokine levels (c). (b, c) are schematic representation: the numbers inside the boxes indicate the Spearman correlation coefficients (r) only for those pairs of cytokines that show statistical significance (p < 0.05). The squares inside the boxes graphically represent the value of r: the light blue color indicates r values between 0 and 1 (positive correlation), and the red color indicates values between −1 and 0 (negative correlation), while its size increases as r increases towards values close to |1|. -P, portal–periportal; -L, lobular. Panel (B) Relationship between intrahepatic cytokine levels and liver damage. Expression levels of intrahepatic cytokines in relation to hepatitis (a) and fibrosis (b) severity. MM, minimal–mild; MS, moderate–severe hepatitis. Advanced fibrosis (F≥3) according to METAVIR. The results are depicted in box plots. Horizontal lines within boxes indicate medians. Horizontal lines outside the boxes represent the 5 and 95 percentiles. Mean is indicated as +. FC, fold change. Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare all data sets, except for IL-1β and IL-23 vs. hepatitis severity for which Student’s t-test was applied.