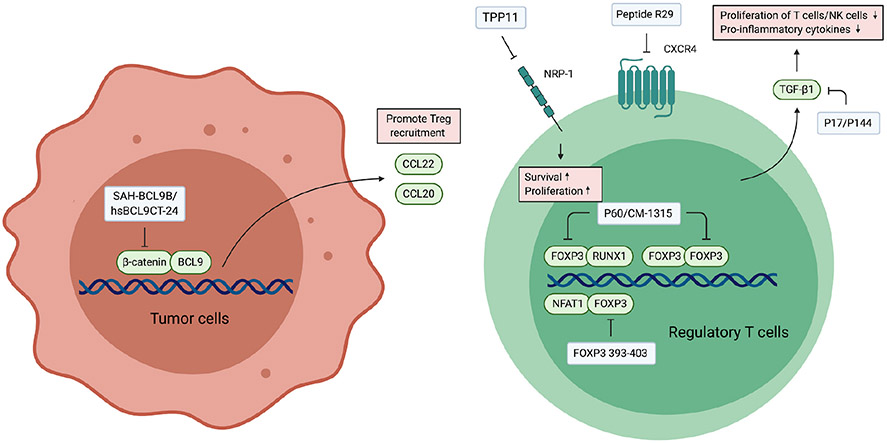
Fig. 3.
Peptides targeting Tregs. FOXP3 is a biomarker of Tregs which forms a complex with numerous transcription factors and chromatin modifying factors to regulate the expression of genes related to Treg differentiation and the maintenance of its immunosuppressive phenotype. Peptides targeting FOXP3 activate transcription factors such as NFAT1 and RUNX1 by releasing them from the inhibition by FOXP3. The activation of these transcription factors leads to the suppression of Treg activity. NRP-1 and CXCR4 are other targets highly expressed in intratumoral Tregs. TGF-β is a major immunosuppressive cytokine secreted by Tregs, and therefore inhibitors for TGF-β suppress the function of Tregs. Inhibition of tumor intrinsic β-catenin suppresses the secretion of Treg recruiting chemokines, which consequently reduce the infiltration of Tregs in the tumor.