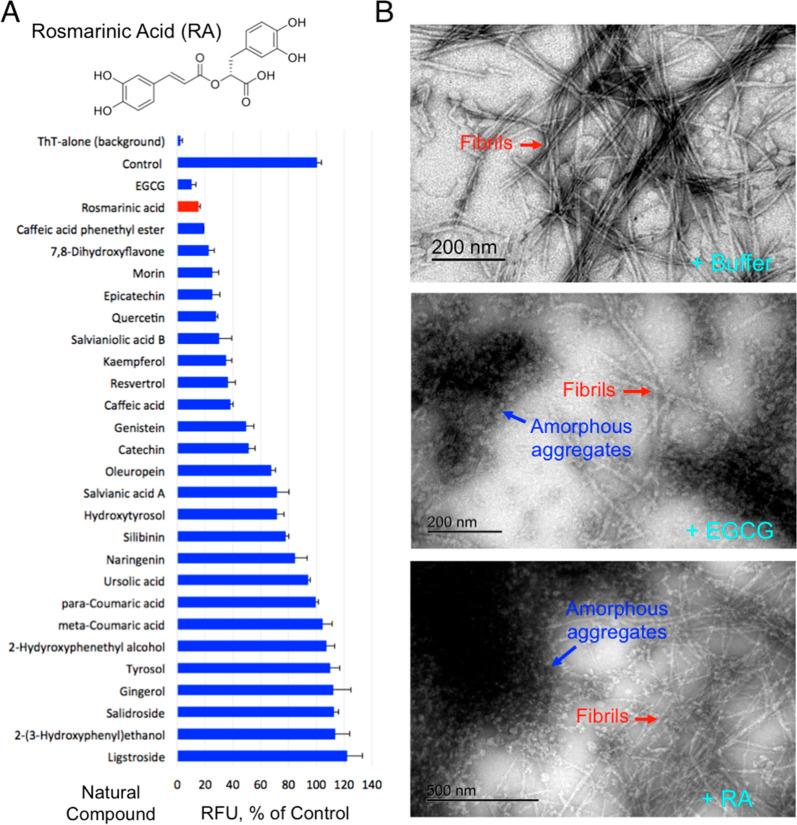
Figure 1.
Identification of RA as a potent amylin amyloid inhibitor. (A) Identification of RA as strong amylin amyloid inhibitor from a natural product library enriched with catechol-containing compounds, a class of broad amyloid inhibitors we recently discovered, using a ThT fluorescence-based screening. EGCG was used as a positive control. Amylin concentration was 5 μM, and the molar ratio of compound to amylin was 2:1. Chemical structure of RA is shown. (B) TEM images of human amylin amyloid with and without inhibitor treatment (1:20 amylin/drug molar ratio). Mature fibrils and amorphous aggregates are indicated by the red and blue arrows, respectively. Buffer treatment sample served as control (100% mature fibril). RA treatment resulted in an estimated 50% mature fibrils and 50% amorphous aggregates, whereas treatment with EGCG, a known strong inhibitor, resulted in similar partial fibrils and partial amorphous aggregates.