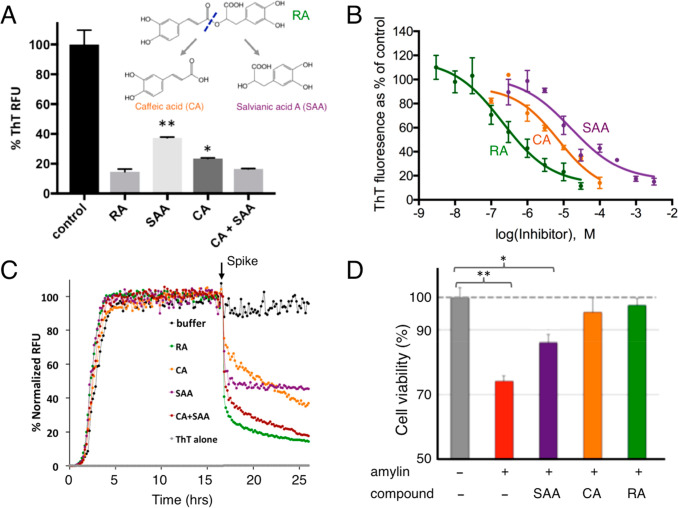
Figure 3.
Additive effects of RA components in amylin amyloid inhibition. (A) ThT fluorescence-based amyloid inhibition assay by RA and its hydrolytic components CA and SAA. Inhibition from a 1:1 molar ratio mixture of CA and SAA is similar to that of RA, but significantly stronger than those from CA or SAA alone. (B) IC50 measurements by ThT fluorescence based inhibition assays. IC50 is estimated to be 200–300 nM for RA, 7.2 μM for CA, and 90 μM for SAA. (C) ThT fluorescence-based amyloid remodeling assay shows amyloid remodeling after spiking of buffer control, RA, CA, SAA, and CA+SAA (1:1 molar ratio) after aggregation reaches a plateau (t = 17 h). (D) Neutralization of amyloid-induced toxicity by RA, CA, and SAA in Neuro2A cells. Amylin concentration was 2.5 μM, and the ratio of the inhibitor/amylin is 5:1. Compared to the control, RA, and to lesser degrees, CA and SAA, significantly neutralize amyloid-induced toxicity. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.