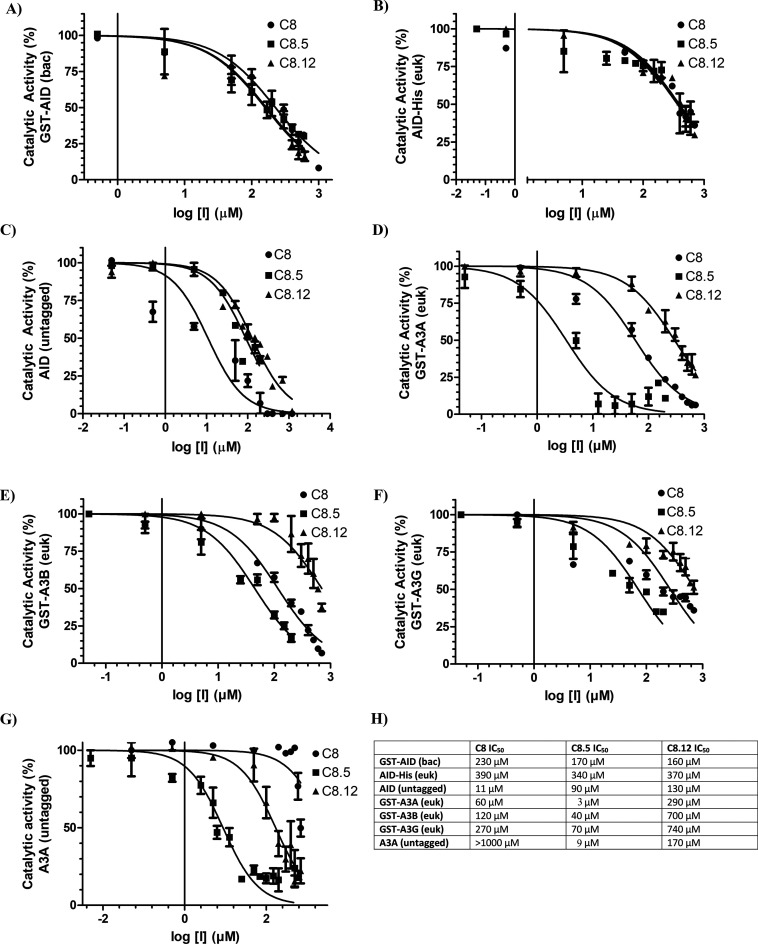
Figure 5.
Structural analogues of C8 exhibit variable potency against AID, A3A, A3B, and A3G. Each panel measured catalytic activity in the presence of C8, C8.5, or C8.12. (A) Bacterially expressed and purifiedGST-AID. (B) Eukaryotic-expressed AID in whole 293T cell lysate. (C) Eukaryotic-expressed native untagged AID in whole 293T cell lysate. (D) Eukaryotic-expressed and purified GST-A3A. (E) Eukaryotic-expressed and purified GST-A3B. (F) Eukaryotic-expressed and purified GST-A3G. (G) Eukaryotic-expressed native untagged A3A in 293T cell lysate. (H) List of C8, C8.5, and C8.12 IC50 values across each enzyme. All experiments used 140 mM DMSO as a negative control, designating 100% enzyme activity. All AID reactions were performed at 37 °C for 2–4 h at pH 7.2 using 2 nM of the standard bubble oligonucleotide substrate TGCbub7. GST-A3A, GST-A3B, GST-A3F, and GST-A3G reactions were incubated at 37 °C for 2 h in pH 5.5 for A3A/B and pH 6.0 for A3G/F using 2 nM of standard single-stranded oligonucleotide substrates containing a single target TTCA motif for A3A, A3B, and A3F and a single target CCC motif for A3G.