Figure 1.
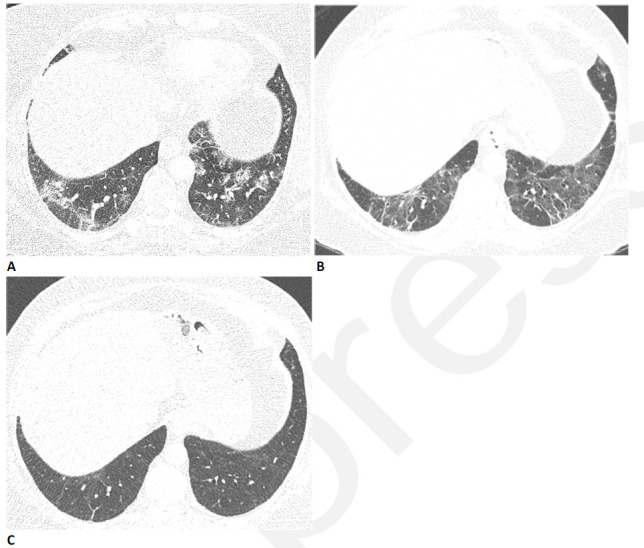
59-year-old woman with sequelae of COVID-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). (A) CT on admission shows patchy consolidation and ground glass abnormality. This subsequently progressed to ARDS. (B) Two months later, the consolidation has resolved but there is moderate ground glass abnormality, multifocal linear abnormality and mild bronchiectasis. (C) Seven months after admission, these abnormalities had almost completely resolved, and restrictive pulmonary function also resolved.
