Figure 12.
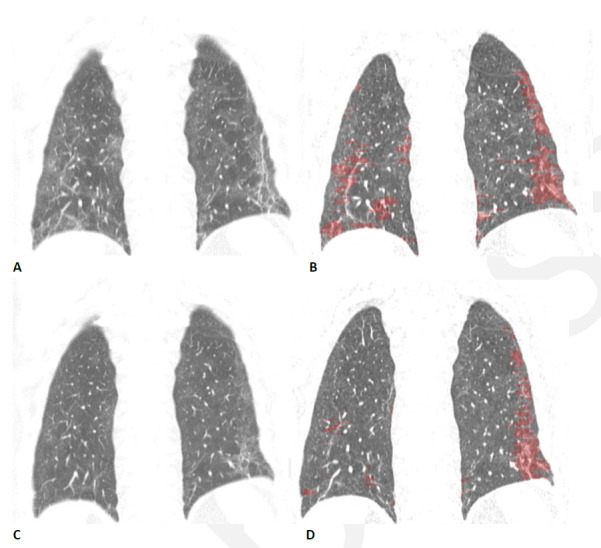
Quantitative CT assessment of linear/reticular abnormality following COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in a 59-year-old woman. (A) Coronal CT obtained ten weeks after onset of infection shows ground glass abnormality with linear and reticular abnormality at both bases. (B) Corresponding quantitative CT image delineates the linear/reticular abnormality, quantified at 10.5% of the lung volume. (C) Four months later, the extent of ground glass and of linear/reticular abnormality has decreased substantially. Symptoms had resolved, and pulmonary function had returned to normal. (D) Corresponding quantitative CT indicates decrease in linear/reticular abnormality, now 4.6%.
