Figure 2.
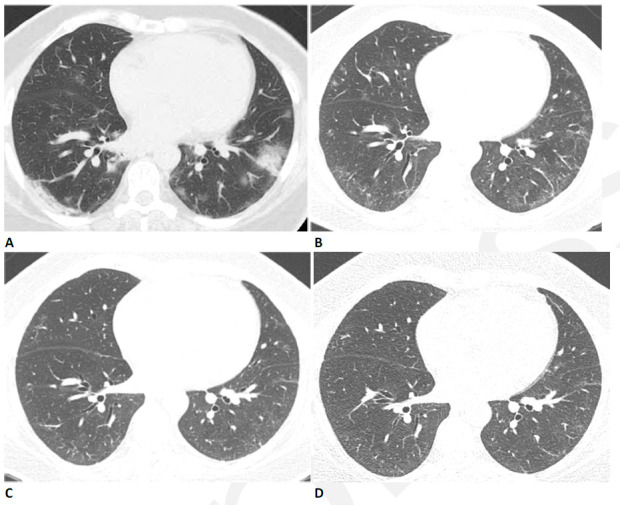
59-year-old woman with sequelae of COVID-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). (A) CT on admission shows patchy nodular consolidation. A halo of ground glass opacity is present around the largest left lower lobe nodule. The patient subsequently developed ARDS. (B) Two months later, the consolidation has resolved with moderate ground glass abnormality. (C) Three months after admission there is further improvement in ground glass. (D) Eleven months after admission there is still mild residual ground glass abnormality, but symptoms had resolved and pulmonary function was normal.
