Figure 6.
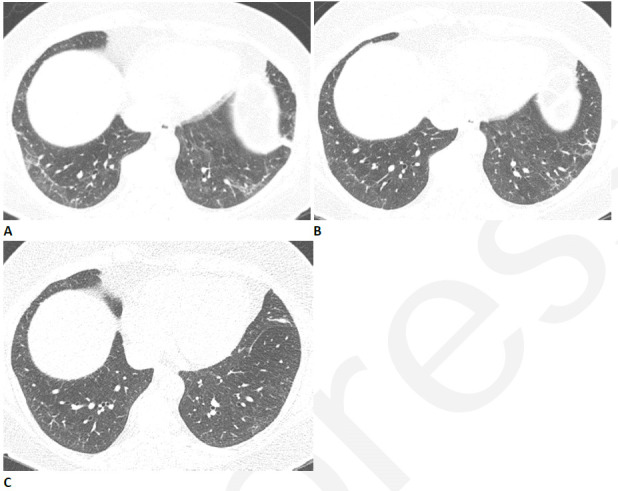
Resolving reticular abnormality and subpleural bands following COVID-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). (A) CT two months after infection shows ground glass abnormality with mild reticular abnormality and subpleural bands. No traction bronchiectasis or architectural distortion is visible. (B) CT six months after infection shows partial clearing. (C) CT eleven months after infection shows near complete resolution, with mild residual ground glass abnormality. Pulmonary function returned to normal.
