Figure 9.
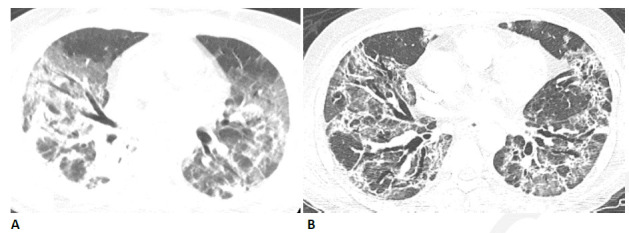
54-year-old man with COVID-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and subsequent fibrosis. (A) CT two weeks after admission shows diffuse ground glass abnormality with reticular abnormality and traction bronchiectasis in the right middle lobe indicating an organizing phase of lung injury. (B) CT six months after admission shows decreased ground glass abnormality but extensive traction bronchiectasis and architectural distortion suggesting fibrosis. The patient remained symptomatic with restricted pulmonary function.
