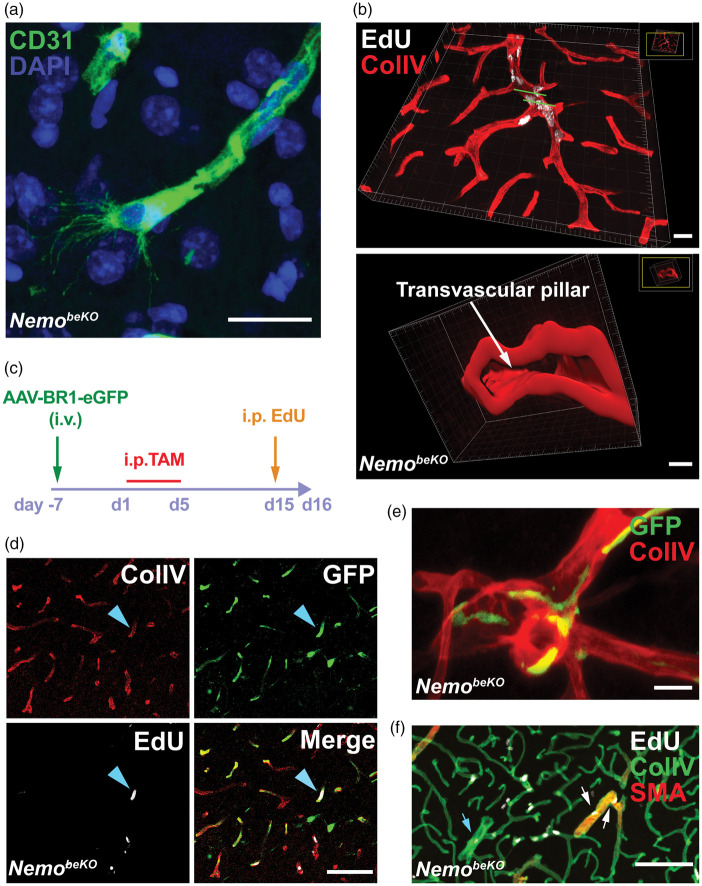
Figure 3.
Angiogenesis in NemobeKO mice affects resident brain endothelial cells in all parts of the vascular tree. (a) Representative immunostaining for CD31 showing a tip cell with filopodia in the cortex of a NemobeKO mouse at day 16 after starting tamoxifen injections. Nuclei are stained by DAPI. Scale bars, 20 μm. (b) A 3D view of cortical vessels from a NemobeKO mouse stained for EdU and ColIV (top). In the bottom panel, a 3D cross-sectional view from the vessel fragment between two green lines in the top panel is presented, showing vessel intussusception. Scale bar, 20 μm (top) and 4 μm (bottom). (c) Scheme illustrating the workflow to label resident brain ECs with the AAV-BR1-eGFP virus before inducing Nemo deletion with tamoxifen and administering EdU. (d) Representative staining for ColIV, EdU and GFP from virus-injected mice showing proliferating resident ECs (EdU+GFP+, blue arrowhead). Scale bar, 100 μm. (e) Representative immunostaining for ColIV and GFP from bone marrow-transplanted NemobeKO mice, showing that bone marrow-derived cells were not ECs. Scale bar, 20 μm. (f) Representative staining for EdU, ColIV, and SMA at day 16 after starting tamoxifen injections, depicting proliferating EdU+ ECs in capillaries, SMA+ arterioles (white arrows) and venules (blue arrows). Scale bar, 100 μm.