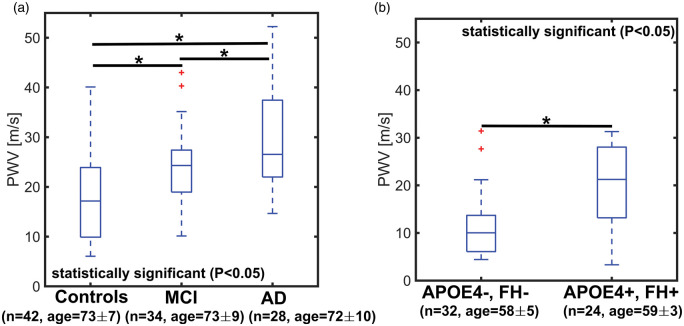
Figure 3.
Boxplots of transcranial pulse wave velocity (PWV) in older controls, mild cognitively impaired (MCI), and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) subjects (a) and middle-age APOE4+, FH+ and controls (e.g. APOE4−, FH−) (b). PWV was estimated from high temporal resolution images derived using a local low-rank (LLR) reconstruction. A statistically higher transcranial PWV was measured in AD (P < 0.001) and MCI (P = 0.013) subjects when compared to age-matched controls. The MCI group appeared to be in transition towards higher transcranial PWV, while AD subjects showed the highest transcranial PWV in this cohort. MCI and AD transcranial PWV were also significantly different (P = 0.029). A statistically higher transcranial PWV (P < 0.001) was measured in middle-age APOE4+, FH+ when compared to middle-aged control adults (APOE4−, FH−), suggesting early vascular changes in subjects with APOE4+, FH+.