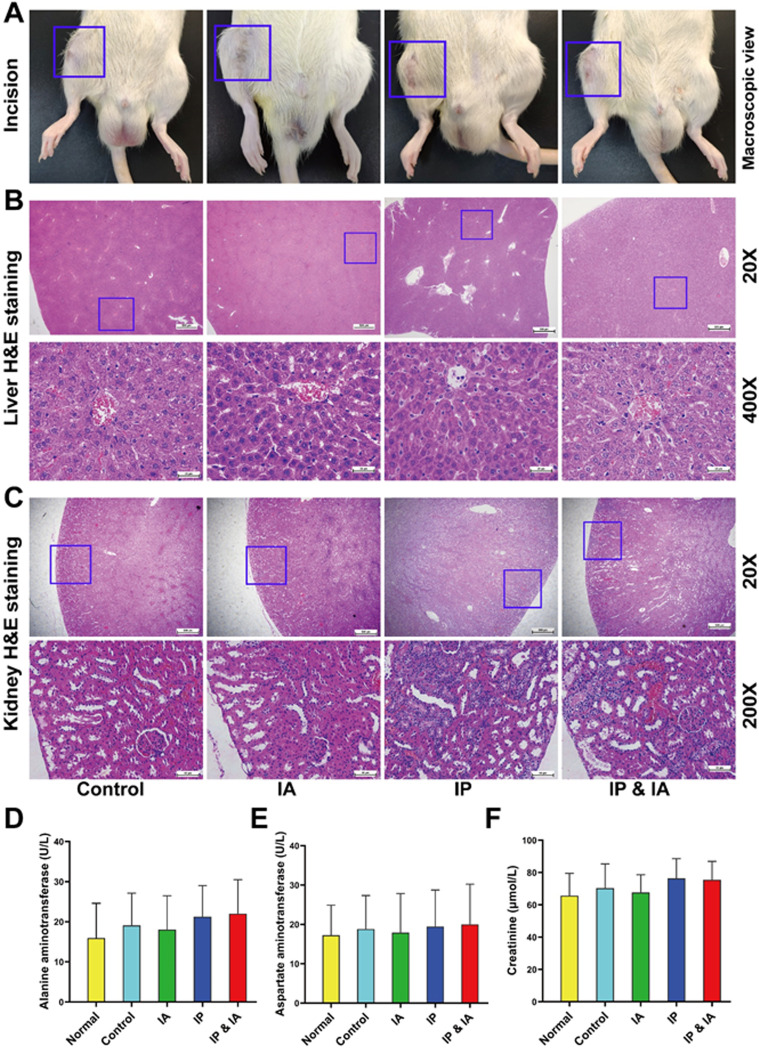
FIG 7.
Photographs of wound healing, pathological H&E staining of the liver and kidney, and liver and kidney biochemical indicator test results for rats with PJI in each group after corresponding treatment. (A) Incision healing of rats. (B) Pathological H&E staining of the liver. (C) Pathological H&E staining of the kidney. (D) Serum ALT levels. (E) Serum AST levels. (F) Serum Cr levels. Normal indicates normal serum biochemical values before surgery. Control (no antibiotics), IP injection of vancomycin (88 mg/kg, q12h), IA injection of vancomycin (44 mg/kg, qd), and IP and IA injection of vancomycin (combined IP treatment at 88 mg/kg, q12h, and IA treatment at 44 mg/kg, qd) were assessed. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (n = 12). The blue boxes in panels A show the incision healing in each treatment group, the blue boxes in panels B show the liver lobular structure of the areas of interest, and the blue boxes in panels C represent the renal cortical region of the areas of interest. Significance was evaluated using a two-way ANOVA for the comparison of serum ALT, AST, and Cr levels in different treatment groups.