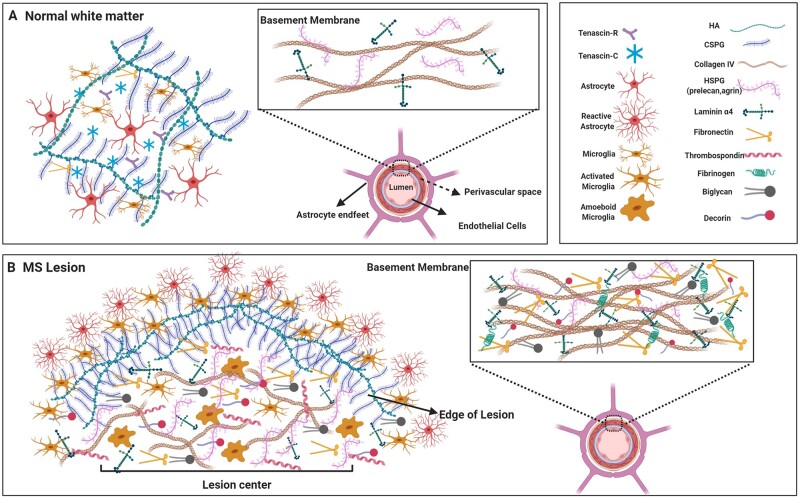
Figure 1.
The ECM in the healthy CNS and in multiple sclerosis lesion. (A) In the uninjured white matter of the CNS, the neural interstitial matrix in the parenchyma primarily consists of CSPGs, hyaluronan (HA) and tenascins whereas collagens (principally type IV), laminins and some members of HSPGs are concentrated in the basement membranes that separate the perivascular space post-endothelial barrier. (B) Several members of the ECM are altered in multiple sclerosis lesions. High levels of CSPGs and hyaluronan accumulate and are prominent at the hypercellular edge as they have been deposited and then cleared from the centre of chronic active multiple sclerosis lesions. As well, fibrillar collagens (I, III, V), small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycans (biglycan, decorin), thrombospondin and the HSPG member (e.g. perlecan) are upregulated in the parenchyma of lesions. Moreover, the basement membranes in multiple sclerosis show a meshwork of ECM components including increased laminins, HSPGs, fibronectin, biglycan, decorin and collagens. Images were created using BioRender.