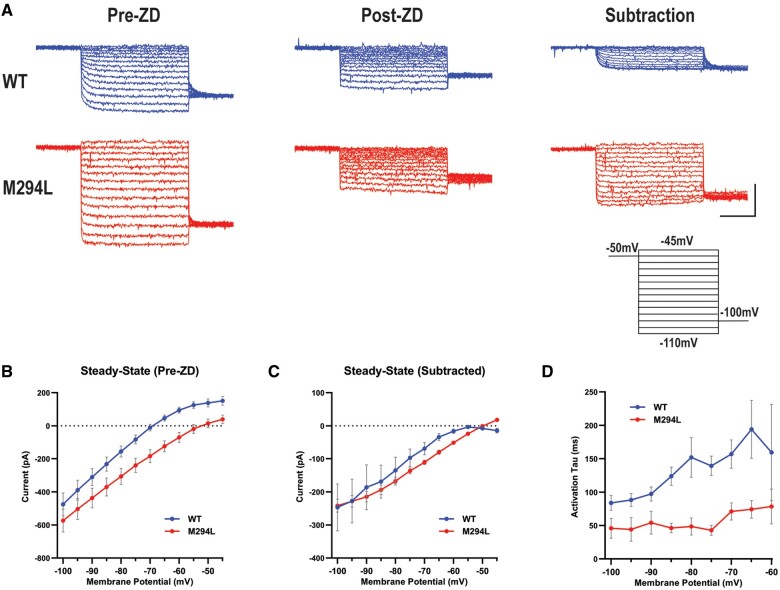
Figure 5.
Ih recorded from Hcn1M294L layer V pyramidal neurons lacks voltage dependence. (A) Representative voltage clamp data from layer V neurons from wild-type (WT) (blue) and Hcn1M294L (red) mice, at baseline (left, ‘pre-ZD’), following the application of ZD 7288 (centre, ‘post-ZD’), and Ih isolated by subtracting ZD 7288-sensitive current traces from baseline traces (right, ‘subtraction’) (scale bar = 1 s, 200 pA). Each dataset shows current traces in response to a series of voltage steps (inset) from the holding potential (−50 mV) to test potentials in the range −110 mV to −45 mV. (B) Current-voltage (I–V) data shows a depolarizing shift in the reversal potential of Hcn1M294L neurons (n = 14) compared to wild-type (n = 12), *P < 0.0001. (C) I–V relationship for Ih from Hcn1M294L neurons (n = 5 wild-type, 5 Hcn1M294L) shows minimal rectification. (D) The activation time constant (tau) of Ih in Hcn1M294L neurons is substantially faster and shows substantially weaker voltage dependence compared to wild-type (n = 5 wild-type, 5 Hcn1M294L).