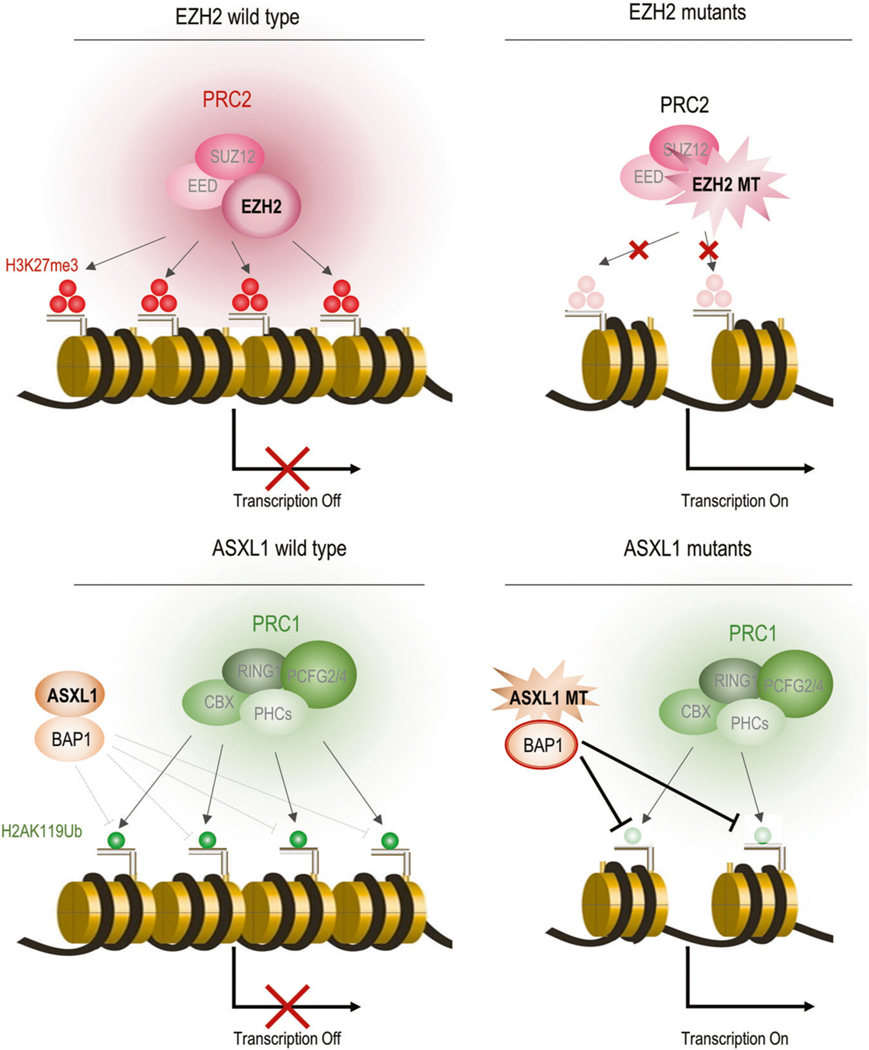
Fig. 2.
Histone modification pathways affected by somatic mutations in MDS. a EZH2 mutants’ mechanisms. EZH2 works as a methylase component of polycomb complex 2 (PRC2) and promotes trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 27 (H3K27me3). It leads to structurally tightened chromatin and negatively regulates transcription of genes. Mutant EZH2 loses its methylase activity and decreases H3K27me3. Transcription factors could easily access DNA and accelerate genetic expression due to loosening histone proteins. b ASXL1 mutants’ mechanisms. ASXL1 promotes ubiquitination of histone H2A at Lysine 119 (H2AK119Ub) through PRC1 by stabilizing BAP1, which negatively regulates H2AK119Ub. It leads to structurally tightened chromatin and negatively regulates transcription of genes. Mutant ASXL1 could not regulate BAP1 so BAP1 is constitutionally activated. This results in decreases in H2AK119U via an enhanced ability to remove H2AK119Ub. Transcription factors can then easily access DNA and accelerate genetic expression due to the loosening of histones