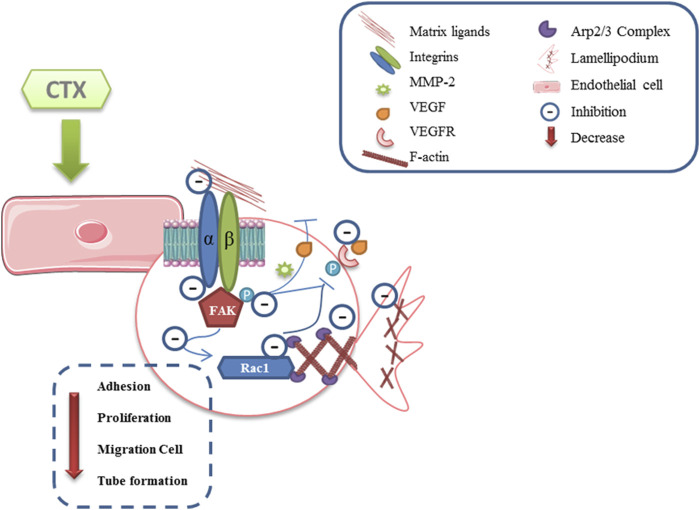
FIGURE 7.
Scheme proposed for anti-angiogenic effect directly induced by CTX. CTX exerts its inhibitory effect by decreasing endothelial cell adhesion to their matrix ligands and, consequently, interferes with FAK kinase phosphorylation, which may lead to the inhibition of Rho GTPases Rac1, since these effector proteins activate the regulation of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Moreover, the inhibitory action on signaling molecules such as FAK may lead to a significant decrease in the secretion of critical mediators for the development of angiogenesis, MMP-2, while reducing speed and persistence of migration in 3D matrices, and of the VEGF, in turn decrease the stimulus on the same receivers. Furthermore, both of inhibited αv and α2 subunits of the integrins, and the decrease in VEGF binding to VEGFR lead to the inhibition of the Arp2/3 complex, a key regulator in actin polymerization and stress fiber formation (Scheme based in Lamalice et al., 2015). Supplementary Material should be uploaded separately on submission, if there are Supplementary Figures, please include the caption in the same file as the figure. Supplementary Material templates can be found in the Frontiers Word Templates file.