Figure 6.
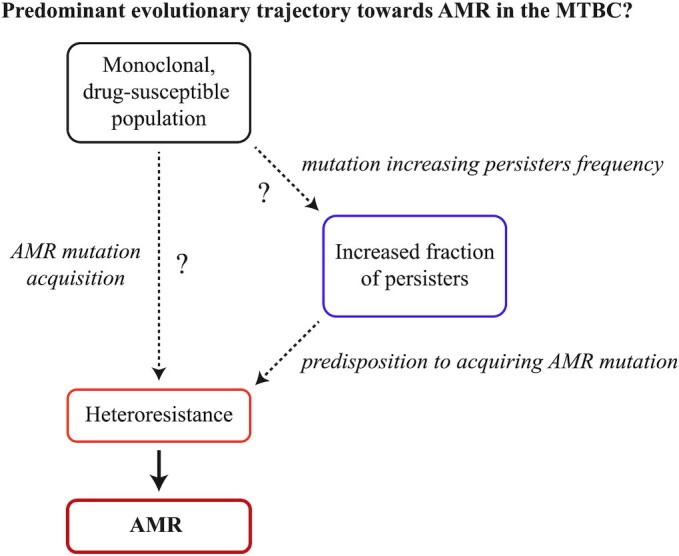
Evolutionary trajectory towards AMR in MTBC. Recent work in other bacteria suggest that mutations that increase the fractions of persisters in the population predispose initially drug-susceptible populations to becoming heteroresistant, and then AMR (Bakkeren et al. 2020; Liu et al. 2020a). Meanwhile, appreciable levels of genetic diversity production has increasingly been shown to occur during the within-host evolution of the MTBC, and likely play a role in the within-host stepwise acquisition of AMR in MTBC observed during treatment. Considering heteroresistance has been documented for essentially all important anti-TB drug, heteroresistance from the spontaneous emergence of AMR mutations is likely an important factor in AMR evolution in the MTBC. However, whether heteroresistance alone or a ‘persisters-mutations-first’ route is the primary evolutionary trajectory towards AMR in the MTBC, requires further investigation.
