Figure 4.
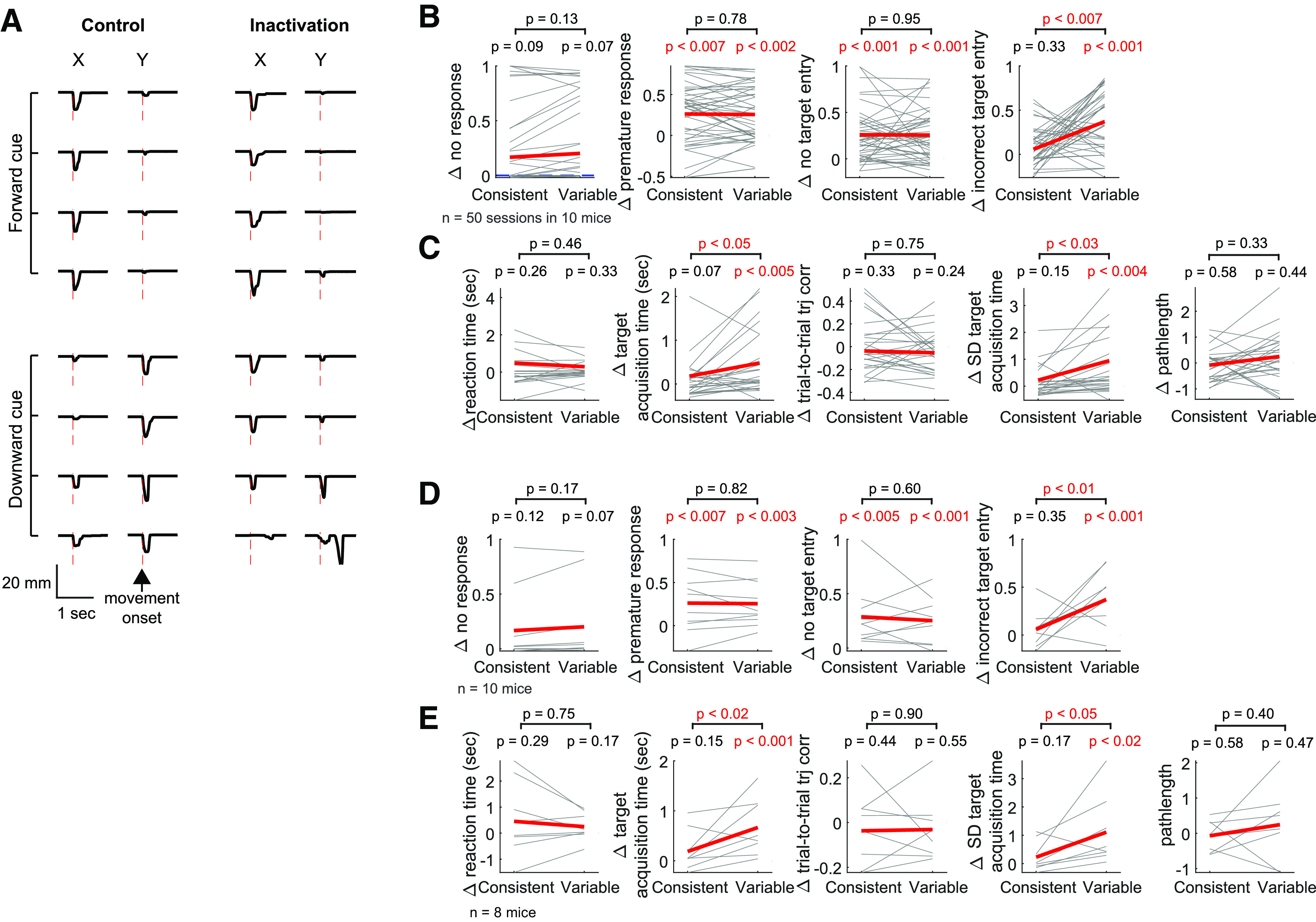
Asymmetric effects of M1 inactivation between the two reach directions. A, Movement trajectories in a control (left) versus inactivation (right) session. Negative displacements along the x axis correspond to movements in the forward direction, whereas negative displacements along the y axis correspond to the downward direction. Top (bottom) traces are movements in response to the forward (downward) drifting gratings. Red vertical lines indicate movement onset. There are incorrect choices in response to the downward drifting gratings in inactivation trials. In this mouse, movements in the forward direction were more consistent than in the downward direction during the last training sessions before the inactivation experiment. B, The effect of M1 inactivation (Δ = inactivation – control) on the fraction of errors. Four types of errors are examined: no response, premature response, no target entry, and incorrect target entry. The consistent and variable directions of each mouse are determined from their last 11 training sessions before the inactivation experiment. Thin lines indicate individual sessions. The direction dependence of inactivation effect was estimated from the slope of a linear mixed-effect model in which the direction is the independent variable and inactivation effect is the dependent variable (see Materials and Methods; Table 1). The red line and pink shade in each plot represent the 95% CI of the fixed-effect slope, and the statistical significance of the slope is also specified. A significant slope indicates that the inactivation effect shows a significant direction dependence. In the fraction of no response, 19 of 50 individual sessions are overlapped as their inactivation effects were zero (i.e., Δ = 0) for both directions. C, The effect of M1 inactivation on the kinematics of movements that successfully entered the correct target. The same illustration format and statistical tests as in B. D, The same as in B, but per animal basis. The average effect was compared between the consistent and variable direction across 10 mice (paired bootstrap test). E, The same as in C, but per animal basis.
