Fig. 3.
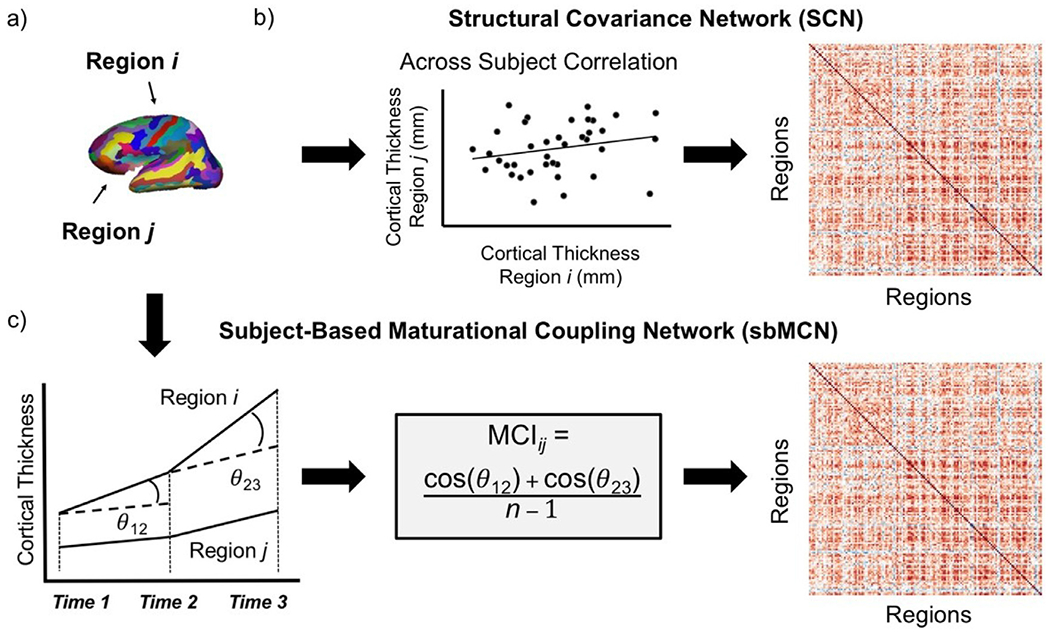
Steps to construct cortical thickness matrices both across and within subjects. a) Regions of interest (ROIs) from the Destrieux brain atlas (Destrieux et al., 2010). b) The construction of a structural covariance network (SCN), which estimates edge strength between nodes as the correlation of cortical thickness across subjects. The resulting matrix used for SCN analysis is a correlation matrix with correlation coefficients as the cells representing the edge strength between each pair of regions. c) The construction of a subject-based maturational coupling network (sbMCN), which estimates edge strength between nodes as the maturational coupling index (MCI) for a subject with available number of timepoints n. Steps to construct an sbMCN depicted here for a subject with 3 timepoints. The resulting matrix used for sbMCN analysis is a maturational coupling matrix with the MCI for a pair of regions as the cells representing the edge strength between each pair of regions. Panel C adapted from Khundrakpam et al. (2019) with permission.
