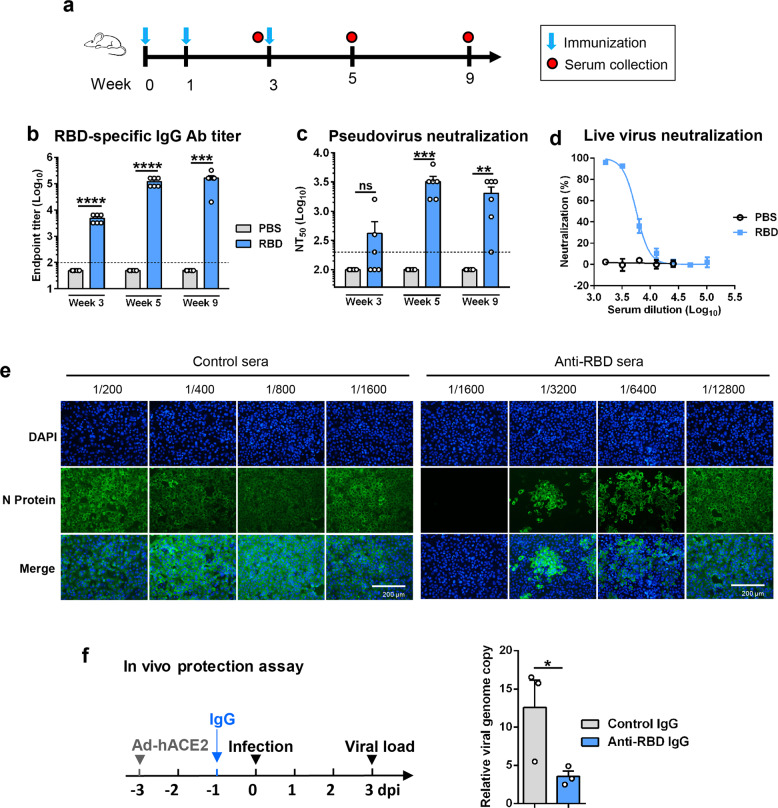
Fig. 2. Immunization with yeast-derived monomeric RBD elicited protective antibodies in mice.
a Immunization schedule. Groups of six BALB/c mice were injected i.p. with alum-formulated monomeric RBD protein (50 μg/dose) or PBS at weeks 0, 1, and 3. Serum samples were collected from individual mice at weeks 3, 5, and 9. b RBD-binding antibody (Ab) titers of the immune serum samples determined by ELISA. Binding titer below 1:100 (the lowest serum dilution; indicated by dashed line) was assigned a value of 1:50 for statistical analysis. c Measurement of neutralization activity of the antisera against SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus. Serum samples that exhibited less than 50% neutralization at the lowest serum dilution (1:200; dashed line) were assigned a NT50 value of 100 for statistical analysis. Each symbol represents one mouse. d, e Neutralization activity of the pooled week-9 antisera against authentic SARS-CoV-2. Live SARS-CoV-2 was incubated with serially diluted antisera and then added to VeroE6 cells. After 48 h culture, the cells were subjected to qRT-PCR (d) or immunofluorescent staining analysis (e). Scale bars, 200 μm. f In vivo protective efficacy of IgG antibody purified from the week-9 antisera against authentic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Left panel: study outline. Ad5-hACE2, recombinant adenovirus 5 expressing human ACE2. Right panel: qPCR results are shown as viral RNA levels relative to GAPDH, using 2−ΔCt method. Each symbol represents one mouse. Data in panels b, c, d, and f are expressed as means ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test and indicated as follows: ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.