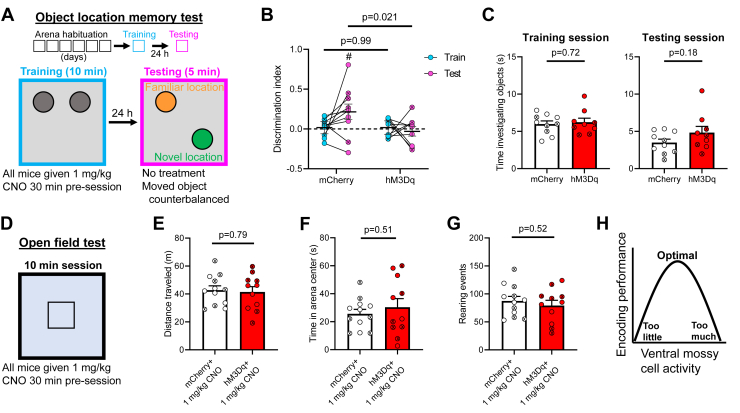
Figure 5.
vMC hyperactivation during object location training impairs retrieval 24 hours later. (A) Schematic of the object location memory test. After 3 days of handling, mice undergo 6 days of habituation to an arena with spatial cues on the wall. The following day, they undergo a 10-minute training session, during which, they are exposed to two identical objects. Twenty-four hours later, they are returned to the arena for a 5-minute testing session where one object has been moved to a novel location and the other remains in the familiar location. CNO (1 mg/kg) was administered 30 minutes before the training session only. (B) CNO administration during training impaired object location memory in mice expressing hM3Dq in vMCs (n = 10 mCherry, n = 9 hM3Dq; virus × session: F1,17 = 3.147, p = .094; virus: F1,17 = 4.338, p = .053; session: F1,17 = 1.192, p = .29). Pairwise comparison p values are shown in the figure. One-sample t test vs. DI = 0: t9 = 2.20, #p = .028. (C) Total time spent investigating both objects did not significantly differ between the mice expressing mCherry (n = 10) or hM3Dq (n = 9) during the training (left; t15.65 = 0.37, p = .72) or testing session (right; t12.65 = 1.40, p = .18). (D–G) Mice were later tested in a 10-minute open field test in an arena with a novel floor surface 30 minutes after administration of 1 mg/kg CNO (n = 12 mCherry, n = 11 hM3Dq) (D). There was no significant difference between mCherry- and hM3Dq-expressing mice in the total distance traveled (t19.74 = 0.27, p = .79) (E), time spent in the arena center (t15.13 = 0.68, p = .51) (F), or number of rearing events (t20.31 = 0.66, p = .52) (G). For panels (B) and (C) and (E)–(G), individual data points containing “X” represent female mice. No mice were excluded because of lack of vMC targeting. (H) Schematic suggesting that a specific setpoint of vMC activity exists for optimal encoding performance, which is supported by previous work showing that inhibition of vMCs impairs spatial encoding (31) and this study suggesting that hyperactivation of vMCs also impairs spatial encoding. CNO, clozapine N-oxide; DI, discrimination index; vMC, ventral mossy cell.