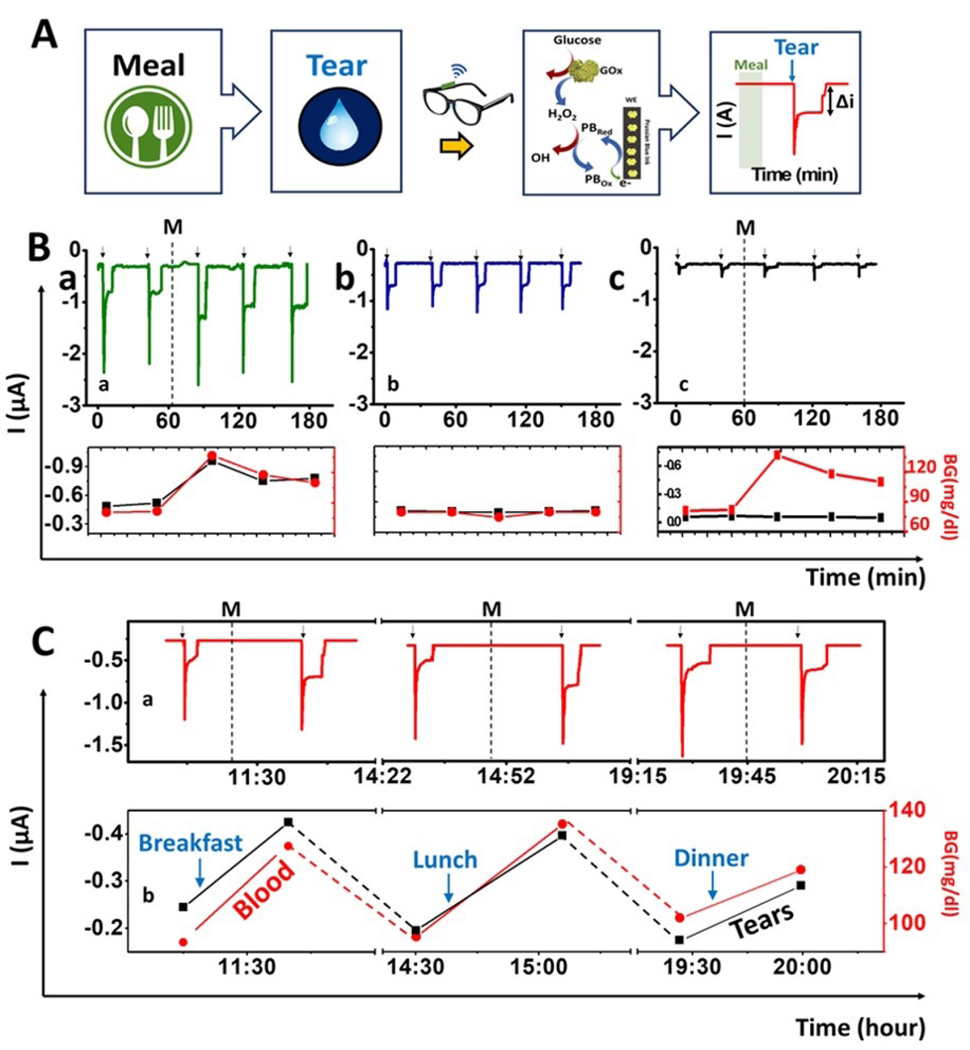
Figure 3. On-body evaluation of tear glucose biosensor.
(A) Scheme of the procedure used for on-body glucose sensing experiments: Tears are stimulated ~15 min after a meal to measure the glucose levels using the GOx-modified PB detector using chronoamperometry. When the tears reach the biosensor, a current change is observed which is proportional to the tear glucose levels. Amperograms showing non-invasive measurement of glucose in tears during 3 h (B) using: a) GOx sensor having meal (M) b) GOx sensor without a meal and c) Prussian blue sensor without enzyme following a meal (M). Bottom: Correlation between current tear signal and the glucose blood level. Red: Blood glucose concentration measured with a glucometer; Black: current intensity obtained with the glasses wearable sensor. (C) Monitoring of glucose levels during the entire day: breakfast, lunch and dinner. Note: Tear stimulation (arrows) and meal (M). Bottom, correlation between blood glucose measurements with a glucometer (red) and the current response of the wearable tear sensor (black). Applied potential, −0.2 V.