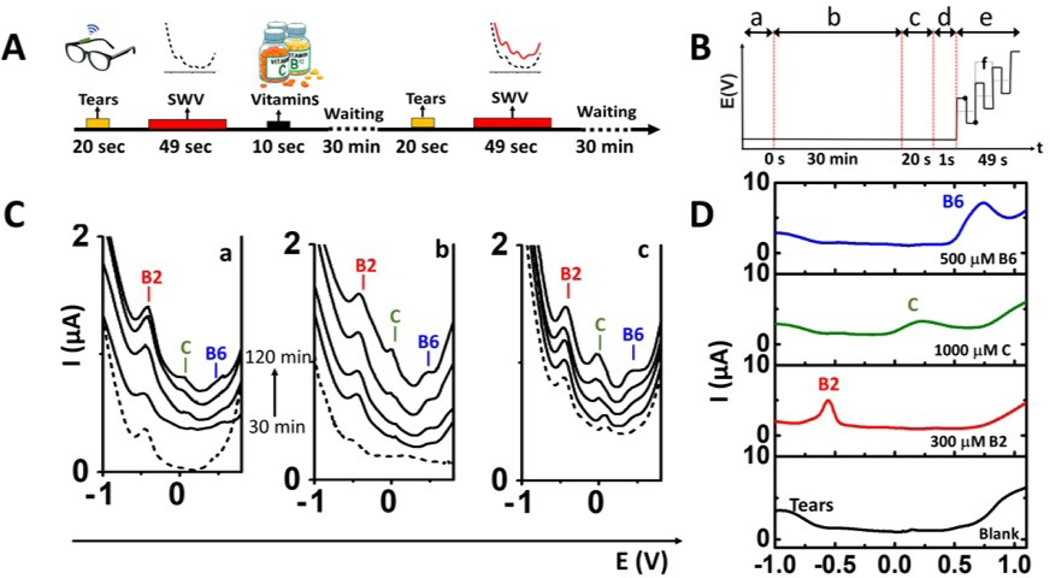
Figure 4. On-body evaluation of tears vitamins sensor.
(A) Scheme of the procedure used for vitamin sensing: Tears are stimulated before taking the vitamins and the device is filled with tears. Once filled, SWV is performed and the baseline is obtained. Then, the device is dried, and the volunteer consumes tables of different vitamins (B2, C and B6). Finally, tears vitamins are monitored every 30 min by SWV. (B) Time-line for the applied potential during the on-body experiments where (a) represents the final of vitamin intake, (b) the waiting time for vitamin absorption by the body, (c) the tears stimulation process, (d) the time to fill the tears fluidic device with the stimulated teardrop and (e) the typical SWV waveform for the multi-vitamin analysis. Where the dots represent the amplitude and “f” the frequency applied. (C) On-body measurements of tears vitamins by SWVs using the eyeglasses flow system for 3 subjects after 30 minutes intervals (30, 60, 90, 120 minutes) of taking vitamin tablets, along with control experiments before taking vitamin (dotted line). (D) Collected tears spiked with standard solutions of vitamins B6 (500 μM, blue plot), C (1000 μM, green plot) and B2 (300 μM, red plot), compared with SWV of collected tears without taking of any vitamin (black plot). SWV Conditions: potential range: −1.0 V- +1.0 V, amplitude: 25mV, frequency: 10Hz.