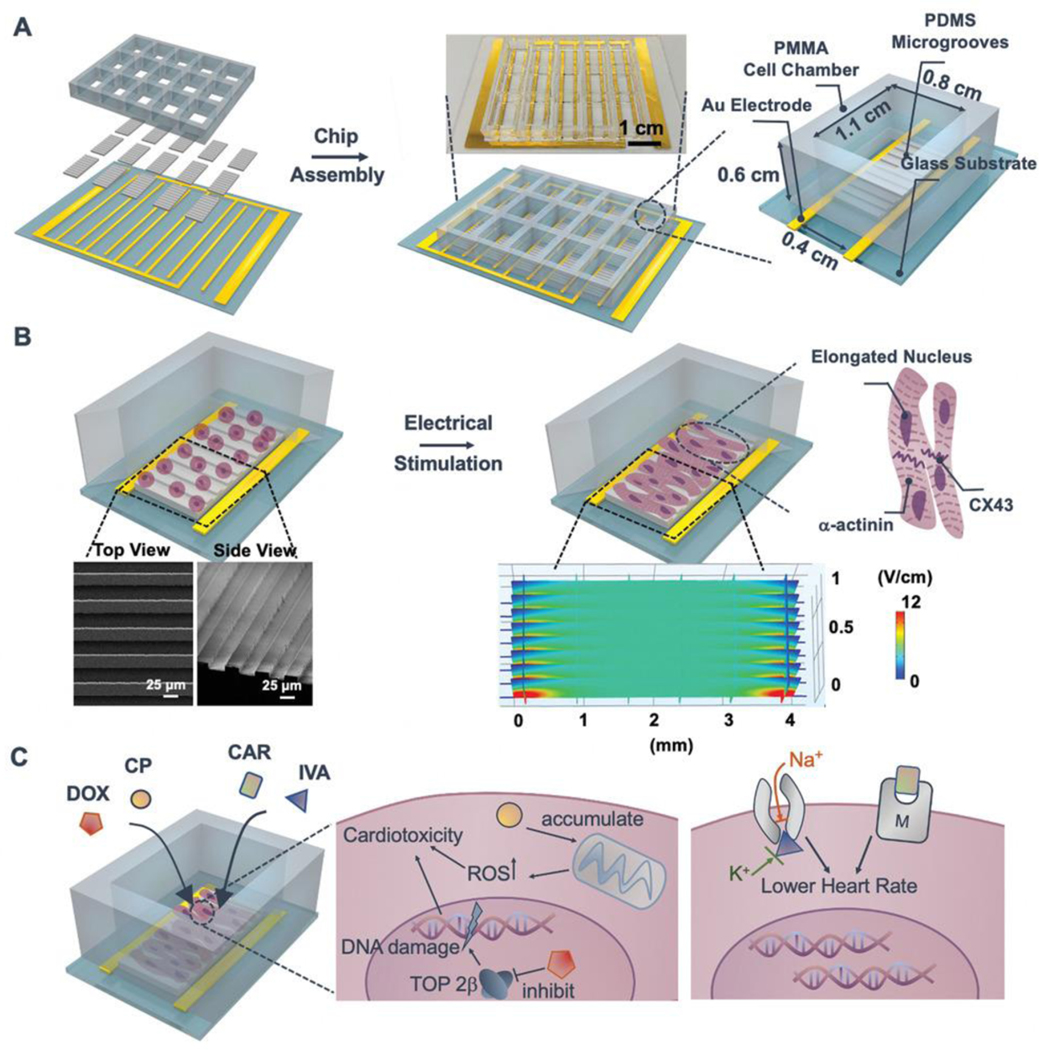
Figure 1.
Schematic for drug screening enabled by the heart-on-a-chip platform. A) The chip is composed of a 3 × 5 PMMA cell culture chamber, PDMS-molded MGs substrate, and comb-structure gold electrode array. Inset: the image of 15-chamber assembled heart-on-a-chip. B) CMs are seeded into MGs embedded chambers on Day 1; electrical stimulation is applied on Day 3 and lasts for 1 day. Enhanced maturation and beating behaviors of CMs are evidenced by increased alignment of α-actinin and CX43. Inset: SEM images of PDMS-based substrates with MGs structure. Inset: COMSOL simulation of the generated electrical field (≈5 V cm−1) within the MG embedded cell culture chamber by electrical pulse stimulation (biphasic, rectangular, 1 ms duration, 3.3 Hz, ±2 V). C) Drug-induced cardiotoxicity (anticancer drugs: DOX and CP) and cardioprotective efficacy (cardioprotective drugs: CAR and IVA) can be screened and evaluated in the heart-on-a-chip. DOX could inhibit topoisomerase II-β (TOP 2β) and cause damage to DNA, while CP could induce the oxidative stress (ROS accumulation) in mitochondria. IVA can block the Na+ and K+ channels to lower the beating rate; CAR is proposed to be the muscarinic (M) receptor agonist with efficacy in reducing heart beating rate.