Abstract
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), or sleeping sickness, is caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei and transmitted through the bite of infected tsetse flies. The disease is considered fatal if left untreated. To identify new chemotypes against T. brucei, previously we identified 797 potent kinase-targeting inhibitors grouped into 59 clusters plus 53 singleton compounds with at least 100-fold selectivity over HepG2 cells. From this set of hits, a cluster of diaminopurine-derived compounds was identified. Herein we report our medicinal chemistry investigation involving exploration of structure-activity and structure-property relationships around one of the HTS hits, N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (1, NEU-1106). This work lead to the identification of a potent lead compound (4aa, NEU-4854) with improved ADME properties, which was progressed into proof-of-concept translation of in vitro antiparasitic activity to in vivo efficacy.
Graphical Abstract

INTRODUCTION
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a group of infectious diseases that affect more than one billion people in 149 tropical and subtropical countries.1 Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as sleeping sickness, is one of the diseases classified as an NTDs by the World Health Organization. There are 65 million people at risk of HAT, and it is usually fatal if left untreated.2, 3 Acc. to WHO, only 1447 new cases were reported in 2017, but HAT still threaten millions in 36 sub-Saharan African countries.4, 5. HAT is caused by the parasite T. brucei which infects the host in two stages. In the first, hemolymphatic phase, parasites stay in the bloodstream and interstitial spaces of the adipose tissue and skin, and then in the second, neurologic phase, the pathogen has crossed the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain, leading to sleep disruption, coma, and death if left untreated.6 As with all NTDs, drug discovery efforts for HAT face numerous challenges, especially the large cost of developing the drug together with the poor financial incentives to big pharma companies.7 Nonetheless, one compound, fexinidazole, was recently approved by the European Medicines Administration,8 and a second (acoziborole) is in the midst of human clinical trials.9
In the resource-constrained field of NTDs, repurposing or repositioning existing drugs has been proven to be quite effective because of reduced costs during discovery and development, the potential to recover and repurpose previously failed compounds, and lower overall risk.7 We have undertaken the repurposing of existing or investigational drugs as starting points for drug discovery. Since T. brucei has been known to express essential kinases that are homologous to human kinases,10–12 we have found that repurposing human kinase inhibitors can be successfully utilized for uncovering antitrypanosomal lead compounds.13–17
Utilizing this so-called “lead repurposing” approach,7 we have previously reported 797 potent and selective inhibitors by high-throughput screening of a kinase library with over 42,000 compounds.18 One of the promising hits from this screening was NEU-1106 (1).18 The targeted properties and profile of compound 1 are listed in Table 1 along with the targeted properties for antitrypanosomal lead compounds. Herein, we report the structure activity relationships (SAR) and structure property relationships (SPR) for analogs of 1 that lead to the discovery of lead compound 4aa (NEU-4854) with improved ADME and physicochemical properties.
Table 1.
Targeted parameters and corresponding values of NEU-1106 (1)
| Targeted Lead Properties | NEU-1106 (1) | |
|---|---|---|
| T. b. brucei pEC50 | ≥7.0 | 7.5 |
| MRC5 pTC50 | <5.0 | 4.3 |
| cLogP | ≤3 | 2.6 |
| PSA | 40< x<90 | 79 |
| LLE | ≥4 | 4.9 |
| Thermodynamic Aqueous solubility (μM) | ≥10 | 69 |
| MW | ≤360 | 314 |
| LogD7.4 | ≤2 | 3.1 |
| CNS MPO score | ≥4 | 4.5 |
| Human PPB (%) | ≤95 | 95 |
| HLM CLint (mL/min/mg protein) | <47 | 64 |
| Rat Hepatocyte CLint (mL/min/106) | <27 | 9.5 |
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Overall, NEU-1106 (1) possesses a good profile as described in Table 1, but it suffers the fact that it has high human liver microsome clearance (64.2 μL/min/mg) and high logD7.4 (3.1). Further, the presence of a thiophene ring is considered as a structural alert in drug design, as the cytochrome P450 metabolism of thiophene can lead to the formation of highly reactive metabolites viz. thiophene S-oxides and thiophene epoxides.19 Hence, in addition to replacement of the thiophene ring, our work was focused on further improving the LLE value by reducing the lipophilicity, which was expected to lead to improved ADME properties.
We followed a four-step systematic strategy. The first approach involves C-2 modifications (tail region) of the diaminopurine core, followed by C-6 modifications (head region). In the third strategy, cross-over compounds were synthesized by choosing combination of best C-2 and C-6 substitutions (head and tail combinations); Finally, core modifications were performed in order to identify new scaffolds that could potentially be pursued against T. brucei.
C-2 substitutions.
The compounds 3 and 4a-4ab were synthesized by utilizing the methods shown in Scheme 1. The C-6 amination of 2,6-dichloro-9H-purine (2) with 2,2,2-trifluoroethylamine under basic conditions at 90 °C yielded compound 3. Compound 3 was then reacted with varying amines via palladium-mediated C-N coupling, nucleophilic substitution (compounds 4a-4m and 4r-4ab), or C-C coupling via Suzuki reaction (4n-4q). Initially the 3-aminothiophene moiety was replaced with aliphatic amines (4a and 4b), which resulted in the improvement of aqueous solubility, but potency was lost. On the other hand, substitutions using a variety of anilines resulted in improvement in potency compared to compound 1 but led to the reduction in solubility. In an attempt to improve the solubility of the aniline-substituted compound 4c, a variety of substitutions were made; fluoro (4k), trifluoromethyl (4l) and N-methylpiperazine (4m) were introduced. The N-methylpiperazine substitution (4m) resulted in improvement of solubility and other ADME properties but the potency was reduced by more than two log units, whereas fluoro (4k) and trifluoromethyl (4l) substitutions did not result in significant changes in potency or solubility as compared to 4c.
Scheme 1.
Synthetic route for compounds 4a-4ab. Reagents and conditions: (a) 2,2,2-trifluoroethylamine, DIPEA, n-BuOH, 90 °C, 16 h (17%); (b) secondary amine, IPA, 80 °C, 16h; (c) amine, HCl, dioxane, microwave, 150 °C, 40 min.; (d) amine, Pd2dba3, XPhos, KOtBu, t-BuOH, 100 °C, 16h; (e) boronic acid, Cs2CO3, Pd(PPh3)4, 2:1 DME/H2O, 150 °C, microwave, 60 min.
The replacement of the thiophene ring with alternative ring systems resulted in varied SAR and SPR trends. Compounds 4t, 4w, 4y and 4z showed promising activity against T. brucei (pEC50 >6). Interestingly, compounds 4v and 4x were found to be inactive, whereas methylation of the pyrimidine or pyrazine ring (compounds 4w and 4y) displayed improved potency. Compound 4z showed excellent aqueous solubility (734 μM) but slightly lower potency compared to 1. Subsequent replacement of the pyrazole N-ethyl with N-methyl 4aa improved the potency and overall physicochemical and ADME properties over other compounds.
Lipophilic ligand efficiency (LLE = pEC50 – cLogP) describes the quality of a lead compound, gauging how much of the potency is due to specific binding interactions versus the general lipophilicity of the compound.20 LLE allows the capture of both potency and lipophilicity in a single parameter.20, 21 Our targeted LLE values for a lead compound is ≥4, as aligned with standard medicinal chemistry practices. Several tested compounds were in excess of this goal. In particular, compound 4aa was found to be the best compound in C-2 substituted series with an LLE value of 5.7 and an appreciably improved physicochemical properties profile. The potency data and in vitro ADME profile of compounds 1, 3 and 4a-4ab are listed in Table 2.
Table 2.
Inhibition profile against T. brucei and in vitro ADME profile of C-2 substituted purines

| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R | T. brucei pEC50a / Log fold Selectivityb | T. brucei LLEc | Aq. sol. (μM) | Human Liver Microsome CLint (uL/min/mg protein) | Rat hepatocyte CLint (uL/min/106 cells) |
| 1 |

|
7.5 / 3.2 | 4.9 | 69 | 64 | 9.5 |
| 3 | -Cl | 4.4 / >0.10 | 2.8 | 705 | < 3 | 8.7 |
| 4a |

|
4.7 / >0.40 | 3.3 | >1000 | < 3 | 6.6 |
| 4b |

|
< 4.4 | -- | >1000 | 14 | 14 |
| 4c |

|
7.8 / >3.5 | 5.0 | 15 | 26 | 10 |
| 4d |

|
7.4 / >3.1 | 4.1 | 20 | 32 | 30 |
| 4e |

|
7.8 / >3.5 | 4.5 | 21 | 89 | 22 |
| 4f |

|
7.6 / 3.3 | 5.0 | 10 | 67 | 48 |
| 4g |

|
7.6 / >3.3 | 5.0 | 55 | 120 | 41 |
| 4h |

|
7.4 / 3.1 | 4.7 | 15 | 26 | 10 |
| 4i |

|
7.8 / 3.3 | 4.4 | 9.0 | 22 | 14 |
| 4j |

|
7.1 / 2.6 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 121 | 47 |
| 4k |

|
7.4 / >3.1 | 4.5 | 46 | 64 | 18 |
| 4l |

|
7.7 / 3.4 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 40 | 9.0 |
| 4m |

|
5.8 / 1.2 | 3.0 | 175 | <3 | 9.8 |
| 4n |

|
5.0 / >0.70 | 1.8 | 10 | 120 | 255 |
| 4o |

|
4.9 / >0.60 | 1.9 | 55 | 209 | 88 |
| 4p |

|
5.5 / >1.2 | 1.7 | 0.70 | 53 | 65 |
| 4q |

|
5.2 / >0.94 | 1.8 | 3.0 | 79 | 7.0 |
| 4r |

|
5.6 / >1.3 | 2.6 | 10 | 161 | 44 |
| 4s |

|
4.8 / >0.50 | 3.2 | 955 | <3.0 | <1.0 |
| 4t |

|
7.0 / >2.7 | 4.1 | 1.0 | 33 | 3.9 |
| 4u |

|
5.5 / >1.2 | 4.0 | 27 | 58 | >300 |
| 4v |

|
4.4 / >0.10 | 2.8 | 358 | 30 | 2.2 |
| 4w |

|
6.2 / >1.9 | 4.5 | 97 | 51 | 21 |
| 4x |

|
5.8 / >1.5 | 4.8 | 5.0 | 23 | 2.7 |
| 4y |

|
6.4 / >2.1 | 5.3 | 3.0 | 162 | 20 |
| 4z |

|
6.2 / >1.9 | 4.5 | 734 | 50 | 2.0 |
| 4aa |

|
6.9 / 2.6 | 5.7 | 212 | 17 | 2.3 |
| 4ab |

|
<5.0 | -- | 135 | 12 | 5.0 |
pEC50=−logEC50
Log fold selectivity = T. brucei pEC50-MRC5 pTC50
LLE (lipophilic ligand efficiency) = pEC50-clogP
Additional ADME data, including Log D7.4 and human plasma protein binding, are included in Table S1 of the supporting information. All SD within ±0.16
The role of the anilino N-H hydrogen bond donor was also investigated by synthesizing compounds by either deletion of the intervening -NH from the C-2 position or by N-methylation (4n-4r). The loss in potency suggested that a hydrogen bond donor is required at the C-2 position.
C-6 substitutions.
The compounds 5a-5aa were synthesized as shown in Scheme 2. The C-6 amination of 2,6-dichloro-9H-purine (2) with the respective amines at either room temp. or heating at 80 °C followed by reaction with 3-aminothiophene or aniline via Buchwald or nucleophilic substitution yielded compound 5. Several analogs were synthesized by replacing the C-6 amine with different primary and secondary amines. Also, some matched pair analogs (5v-5z) were synthesized with aniline at the C-2 position to observe the variations in SAR and SPR comparing the 3-aminothiophene substitution with its aniline bioisostere.22 The replacement of the terminal CF3 group of 1 with CH3 (5b) resulted in little change in the potency, an increase in solubility, and a decrease in metabolic stability as compared to 1.
Scheme 2.
Synthetic route for compounds 5a-5ae. Reagents and conditions: (a) amine, THF, rt, 16 h; (b) amine THF:IPA (1:1), 80 °C, 4h; (c) amine, HCl, dioxane, microwave, 150 °C, 40 min.; (d) amine, Pd2dba3, XPhos, KOtBu, t-BuOH, 100 °C, 16h.
In addition, a set of analogs with varied numbers of carbon atoms (n=1–4) was synthesized (compounds 5a-5d). In general, with the increase in carbon length potency increased but microsomal clearance increased as well. Compound 5d was very potent against T. brucei (pEC50 = 8.0) but high clearance was observed. Though we had assumed that a terminal trifluoromethyl group would improve metabolic clearance properties (c.f. 1 versus 5b), this approach did not pay dividends in improving the properties (c.f. 5d vs. 5e).
Several other primary and secondary aliphatic amines were added to the C-6 position while keeping the thiophene ring constant at the C-2 position. Similarly, a few matched pair analogs with the aniline bioisostere at the C-2 position were also synthesized. Overall, compounds 5f, 5m, 5q and 5v were found to be improved among different C-6 substituted aliphatic amines, showing low metabolic clearance, good aqueous solubility and acceptable potency range. The potency data and in vitro ADME profile of compounds 5a-5aa are listed in Table 3.
Table 3.
Inhibition profile against T. brucei and in vitro ADME profile of C-6 substituted purines

| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R1 | R2 | T. brucei pEC50a / Log fold Selectivityb | T. brucei LLEc | Aq. sol. (μM) | Human Liver Microsome CLint (uL/min/mg protein) | Rat hepatocyte CLint (uL/min/106 cells) |
| 5a |

|
A | 6.0 / >1.4 | 5.0 | 621 | 39 | 79 |
| 5b |

|
A | 7.2 / >2.3 | 5.0 | 515 | 135 | 29 |
| 5c |

|
A | 7.5 / >2.9 | 4.1 | 159 | 300 | 136 |
| 5d |

|
A | 8.0 / >3.7 | 4.0 | 21 | 282 | 62 |
| 5e |
|
A | 7.9 / >3.6 | 4.7 | 32 | 300 | 80 |
| 5f |

|
A | 7.2 / >2.9 | 4.8 | 55 | 69 | 6.0 |
| 5g |

|
A | 5.9 / >1.6 | 4.5 | 389 | 66 | 45 |
| 5h |

|
A | 7.5 / >3.2 | 4.1 | 34 | 139 | 65 |
| 5i |

|
A | 7.7 / >3.4 | 3.2 | 34 | 81 | 19 |
| 5j |

|
A | 6.3 / >2.0 | 1.8 | 855 | 47 | 45 |
| 5k |

|
A | 7.4 / >3.1 | 1.7 | 23 | 95 | 24 |
| 5l |

|
A | 7.3 / >3.0 | 1.9 | 24 | 93 | 123 |
| 5m |

|
A | 6.9 / >2.6 | 1.8 | 87 | 24 | 12 |
| 5n |

|
A | 7.2 / >2.9 | 3.0 | 57 | 87 | 38 |
| 5o |

|
A | 7.0 / >2.7 | 4.0 | 407 | 191 | 28 |
| 5p |

|
A | 7.4 / >3.1 | 4.5 | 53 | 96 | 65 |
| 5q |

|
A | 7.1 / >2.5 | 4.4 | 304 | 46 | 10 |
| 5r |

|
A | 7.1 / >2.2 | 4.7 | 204 | 137 | 215 |
| 5s |

|
A | 7.7 / >3.4 | 5.0 | 95 | 258 | 107 |
| 5t |

|
A | 7.6 / 3.1 | 4.5 | 33 | 138 | 38 |
| 5u |

|
A | 5.9 / >1.6 | 3.3 | 544 | 10 | 6.7 |
| 5v |

|
B | 7.1 / >2.8 | 4.5 | 35 | 18 | 13 |
| 5w |

|
B | 6.6 / >2.3 | 5.3 | >1000 | 56 | 66 |
| 5x |

|
B | 7.5 / >3.2 | 2.8 | 41 | 27 | 86 |
| 5y |

|
B | 7.4 / >3.1 | 4.0 | 459 | 186 | 48 |
| 5z |

|
B | 6.4 / >2.1 | 2.6 | >1000 | 36 | 17 |
| 5aa | -NH2 | C | <4.4 | 5.7 | >1000 | 33 | 45 |
pEC50=−logEC50
Log fold selectivity = T. brucei pEC50-MRC5 pTC50
LLE (lipophilic ligand efficiency) = pEC50-clogP
Additional ADME data, including Log D7.4 and human plasma protein binding, are included in Table S1 of the supporting information. All SD within ±0.11
Crossover C-2 and C-6 substitutions.
The crossover compounds (5ab-5ad, Table 4) were designed by selecting the best tail substitution at C-2 (4-amino-1-methylpyrazole) with other selected amines at C-6 position. The compounds were synthesized by the procedure described in Scheme 2. Compounds 5ae and 5ac resulted in improvement of potency compared to 4aa, however the clearance rate was also increased. Two others, 5ad and 5ab, did show better solubility and ADME properties but reduced in potency by 0.6 −1.0 log unit compared to compounds 5u and 5f respectively.
Table 4.
Inhibition profile against T. brucei and in vitro ADME profile of cross-over analogs

| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R1 | T. brucei pEC50a / Log fold Selectivityb | T. brucei LLEb | Aq. sol. (μM) | Human Liver Microsome CLint (uL/min/mg protein) | Rat hepatocyte CLint (uL/min/106 cells) |
| 5ab |

|
6.6 / 1.9 | 5.9 | 530 | 23 | 3.2 |
| 5ac |
|
7.3 / 3.0 | 5.5 | 140 | 146 | 25 |
| 5ad |

|
4.9 / >0.60 | 4.2 | 852 | 3 | -- |
| 5ae |

|
7.4 / >3.1 | 5.8 | 176 | 207 | 70 |
pEC50=−logEC50
Log fold selectivity = T. brucei pEC50-MRC5 pTC50
LLE (lipophilic ligand efficiency) = pEC50-clogP
Additional ADME data, including Log D7.4 and human plasma protein binding, are included in Table S1 of the supporting information. All SD within ±0.12
Core modifications.
The modification of the core structure was performed as described in Schemes 3–4 by replacing the purine scaffold with pyrimidine, quinazoline and thienopyrimidine, or by N-methylation of the imidazopyrimidine to explore the role of the hydrogen bond donor at N6. All the core modifications resulted in loss of activity except for the thienopyrimidine substitution (compound 10) which showed moderate potency against T. brucei with pEC50 value of 6.4. The potency data and in vitro ADME profile of core modified compounds 9a-11 and 13a-b are listed in Table 5.
Scheme 3.
Synthetic route for compounds 9–11. Reagents and conditions: (a) 2,2,2-tifluoroethylamine, DIPEA, n-BuOH, 90 °C, 16 h; (b) amine, Pd2dba3, XPhos, KOtBu, t-BuOH, 100 °C, 16h.
Scheme 4.
Synthetic route for compounds 13a-13b. Reagents and conditions: (a) 2,2,2-tifluoroethylamine, DIPEA, n-BuOH, 90 °C, 16 h; (b) aniline, HCl, dioxane, microwave, 150 °C, 40 min.; (c) 3-aminothiophene, Pd2dba3, XPhos, KOtBu, t-BuOH, 100 °C, 16h.
Table 5.
Inhibition profile against T. brucei and in vitro ADME profile of core modified analogs

| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | R | T. brucei pEC50 a / Log fold Selectivityb | T. brucei LLEc | Aq. sol. (μM) | Human Liver Microsome CLint (uL/min/mg protein) | Rat hepatocyte CLint (uL/min/106 cells) |
| 9a |

|
5.1 / >0.80 | 2.2 | 60 | 154 | 44 |
| 9b |

|
5.3 / >1.0 | 3.8 | 47 | 51 | 8.7 |
| 10 |

|
6.4 / 2.1 | 2.1 | 12.3 | 144 | 56 |
| 11 |

|
5.4 / 0.70 | 1.0 | 6.9 | 58 | 68 |
| 13a |

|
5.0 / >0.70 | 2.0 | 451 | >300 | 100 |
| 13b |

|
4.9 / >0.60 | 1.6 | 200 | >300 | 115 |
pEC50=−logEC50
Log fold selectivity = T. brucei pEC50-MRC5 pTC50
LLE (lipophilic ligand efficiency) = pEC50-clogP
Additional ADME data, including Log D7.4 and human plasma protein binding, are included in Table S1 of the supporting information. All SD within ±0.090
The highlights of structure activity relationship (SAR) and structure property relationship (SPR) around lead compound 4aa are depicted in figure 2.
Figure 2.
Key SAR and SPR points around this series for anti T. brucei activity (4aa, NEU-4854)
Cell permeability, metabolic studies and kinase profiling.
Based upon overall profile of potency and in vitro ADME properties, compound 4aa was selected for further studies including Caco-2 permeability studies, mouse plasma stability, mouse liver microsome clearance and CYP450 induction. The results in Table 6 show compound 4aa does not have CYP3A4 induction liability. Though the compound is permeable to Caco-2 cells, it is rapidly effluxed. The compound was also found be to stable in mouse liver microsome and plasma stability assays. Since this chemotype originated from a kinase-targeted library screen, we decided to profile compound 4aa against a panel of human kinases at 5 μM (supporting information Figure S1). Though compound 4aa was found to inhibit several human kinases, it did not show any toxicity in animal efficacy studies and against in vitro cell toxicity assays. Additionally, we have tested compound 4aa against TbMAPK6 (K5140) which is essential for the life cycle of T. brucei and was found to be a better inhibitor over parent compound 1 with IC50 values of 1.2 and 7.6 μM respectively (see supporting information for details). However, moderate inhibition of enzyme suggests this is not the target of action for this series.
Table 6.
Caco-2 permeability data, mouse plasma stability, liver microsome stability and CYP450 induction of compound 4aa
| Entry | Caco-2 Mean Papp A-B (106 cm/s) | Caco-2 Mean Papp B-A (106 cm/s) | Efflux Ratio | Mean A-B Recovery (%) | Mean B-A Recovery (%) | A-B Permeability Ranking | Mouse Plasma Stability % remaining at 60 min | Mouse Liver Microsome (CLint) (mL/min/g liver) | CYP3A4 fold induction (at 10 μM) | CYP3A4 % inhibition (at 10 μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4aa | 5.8 | 44 | 7.6 | 87 | 102 | Higher | 98 | 4.1 | 0.17 (No induction) | 33 |
Pharmacokinetics and efficacy studies of compound 4aa in acute mouse model of HAT.
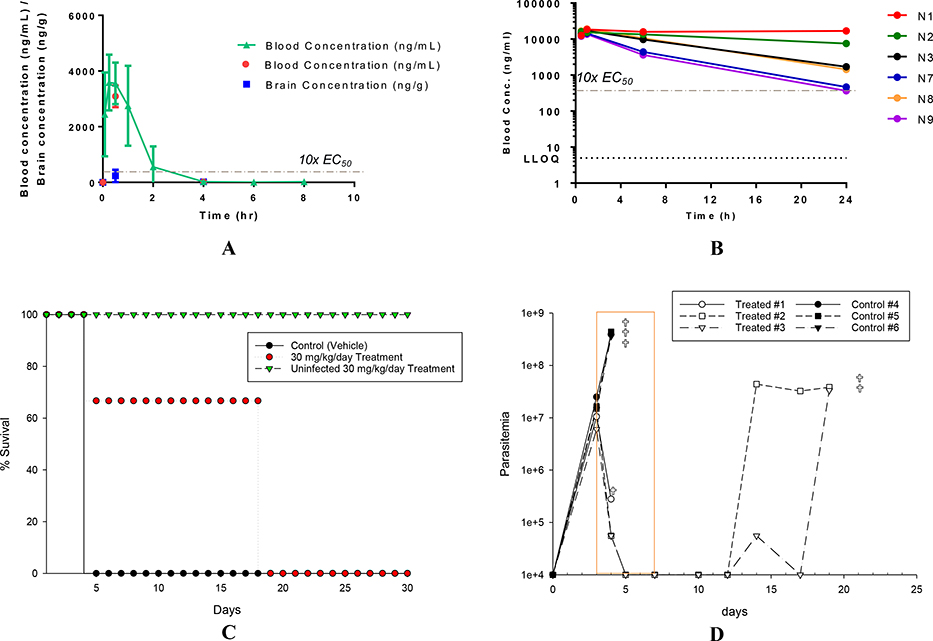
All animal studies were ethically reviewed and carried out in accordance with European Directive 2010/63/EEC and the GSK Policy on the Care, Welfare and Treatment of Animals. The compound 4aa was selected for in vivo studies based upon its overall properties (Table 7). Compound 4aa showed the best combination of potency with selectivity over mammalian cells, favorable physicochemical and in vitro ADME properties. Pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters were measured in plasma of female NMRI mice following an IP dose of 10 mg/kg of 4aa. The peripheral blood levels of 4aa is shown in Figure 3A. The mean Cmax of 4aa was found to be 3670 ng/mL (11.75 μM) (Table S2) and this concentration is approximately 95-fold higher than the EC50 of 4aa (0.123 μM). However, the compound appears to be cleared quickly in mice with t1/2 = 0.76 h (Figure 3A). Blood and brain ratios of 4aa at 0.5 and 4 hours after the administration are shown in Table S3.
Table 7.
Summary table of compound NEU-4854 (4aa)
| Parameters | NEU-4854 (4aa) |
|---|---|
| T. b. brucei pEC50 | 6.9 |
| MRC5 pTC50 | 4.3 |
| cLogP | 1.2 |
| PSA | 96 |
| LLE | 5.7 |
| Thermodynamic Aqueous solubility (μM) | 212 |
| MW | 312 |
| LogD7.4 | 1.9 |
| CNS MPO score | 5.0 |
| Human PPB (%) | 72 |
| HLM CLint (mL/min/mg) | 17 |
| Rat Hepatocyte CLint (mL/min/10×6) | 2.3 |
| Mouse Liver Microsome (CLint) (mL/min/g liver) | 4.1 |
| CYP3A4 Liability | No |
| Mouse plasma stability | Stable |
| Caco-2 permeability | Permeable |
Figure 3.
(A) in vivo pharmacokinetics data of 4aa at dose 10 mg/kg ip in non-infected female NMRI mice; (B) in vivo pharmacokinetics data of 4aa at dose 30 mg/kg ip after ABT-pretreatment in Tbb STIB795 infected mice (N1-N3) and uninfected mice (N7-N9) on day 1 of treatment; (C) percentage survival of animals in acute in vivo murine HAT model (NMRI mice; T. brucei brucei STIB795 parasites); (D) Parasitemia levels graph in murine HAT model, cross indicates the day of death, values represented on the x axis indicate undetected parasitemia (values below 104 parasites/ml which cannot be detected by counting in the Neubauer chamber). Start of infection (arrow) and treatment period (orange box) indicated.
We aimed to achieve plasma drug levels of more than 10x EC50 for 4–6 h; as shown in Figure 3A, this goal is accomplished for under four hours. Noting the rapid clearance, in order to achieve the targeted drug levels and to provide a means to perform proof-of-concept efficacy experiment, we both elevated the IP dose to 30 mg/kg and utilized 1-aminobenzotriazole (ABT) pre-treatment in the mouse efficacy model of HAT disease. ABT is known to inhibit cytochrome P450 and it has been used to increase the exposure of co-administered molecules.23, 24 Indeed, the modified studies indicated increased exposure levels of 4aa with ABT pre-treatment, demonstrating 10x EC50 for beyond 24 hours in both infected and uninfected mice (Figure 3B). The pharmacokinetic parameters are summarized in (Table 8).
Table 8.
Blood pharmacokinetic parameters of 4aa at intraperitoneal administration of 10 mg/kg without ABT-pretreatment and 30 mg/kg (target dose) after ABT-pretreatment to female NMRI mice (infected and non-infected) on day 1 of treatment.
| Mouse type | Dose (mg/kg) | Mean Cmax (ng/mL) ± SD | Mean tmax (h) | Mean t1/2 (h) | Mean AUC0-t (ng·h/ml) | Mean AUC (ng·h/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-infected | 10 | 3670 ± 922 | 0.25–0.5 | 0.758 ± 0.290 | 5340 ± 2860 | 5350±2870 |
| Non-infected | 30 + ABT | 15767 ± 3007 | 0.5–2.0 | 0.638 ± 0.047 | 51799 ± 15424 | 52521 ± 16034 |
| Infected | 30 + ABT | 17267 ± 1258 | 0.5–2.0 | 1.58 ± 1.11 | 77666 ± 15686 | 83443 ± 26918 |
The pharmacokinetic parameters of ABT pre-treated infected and uninfected mice dosed with 4aa were also measured on the fifth days of dosing; significant improvement in the exposure levels was observed (Table S4; and Figure S1).
The efficacy studies were performed in female NMRI mice infected with T. brucei brucei STIB795 parasites. All groups of animals were pre-treated with ABT (50 mg/kg po). The treatment with 4aa (30 mg/kg, ip, once daily) was started from day 3 following infection and continued until day 7. The parasitemia levels in control (untreated) infected animals reached 108/mL on day 4 and all control animals died on day 5, whereas treated groups of animals showed reduction in parasitemia levels compared to control animals on day 4 (Figure 3E). The survival rate of treated groups was increased by 18 days post-treatment (Figure 3D). The uninfected mouse treated with 4aa did not show any signs of toxicity and all animals survived until the end of the studies (Figure 3D). During the experiment, one infected mouse showed some signs of lethargy after two days of treatment and was humanely euthanized. This study identifies compound 4aa as a promising lead for the treatment of HAT, however further studies are required to identify a dosing regimen for the complete cure of infection in mice, and to increase brain penetration.
African animal trypanosomiasis (AAT).
T. brucei, Trypansoma congolense and Trypanosoma vivax are all known to cause AAT in wild and domestic animals. AAT is a significant cause of mortality amongst livestock and has a large economic impact on the development of agriculture in Africa. We have tested our lead compound 4aa against AAT- causing parasites, T. congolense and T. vivax, and it was found to inhibit proliferation of T. congolense and T. vivax with EC50 values of 1.1 and 2.7 μM respectively. Thus, compound 4aa can also be further utilized as a starting point for the discovery of agents for the treatment of AAT.
CONCLUSION
Utilizing a lead repurposing approach, a collection of analogs of the HTS hit NEU-1106 (1) were synthesized and assessed for biological activity against T. brucei and their ADME properties were measured. Structure activity relationships and structure property relationships have been established, leading to the discovery of a potent anti-trypanosomal agent (4aa, NEU-4854) with improved ADME properties. Compound 4aa was advanced to efficacy studies in a mouse model of HAT and it increased the survival time of infected animals by 18 days post treatment at 30 mg/kg. Work is ongoing to identify a dosing regimen of 4aa for the complete cure of infection in mice; and to explore the potential of a new chemotype (10) for anti-trypanosomal activity which was identified here using scaffold replacement strategy.
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
General Chemistry.
All reagents and starting materials were procured commercially from Sigma-Aldrich Inc., Fisher Scientific or Combi-blocks, and used as received. Melting points were recorded on Thermo Scientific MEL-TEMP apparatus. NMR spectra were obtained on a Varian NMR system, operating at 400 MHz and 500 MHz. Chemical data for protons is reported in parts per million (ppm) downfield from tetramethylsilane and are referenced to the residual proton in the NMR solvent [(CD3)2SO, 2.50; CD3OD, 3.31; CDCl3, 7.26; (CD3)2CO, 2.05; ppm]. LCMS analysis was performed using a Waters e2795 Alliance or Waters e2695 Alliance or Agilent 1100 reverse-phase HPLC-MS and 3.5 μm Waters SunFire C18 4.6 × 50mm column, with multiwavelength photodiode array detector (λ = 200–600 nm) and MicroMass ZQ single quadrupole mass spectrometer (electrospray ionization). Gradients for the LCMS analysis was water or acetonitrile, both with 0.1% v/v formic acid (Method A: 5% acetonitrile to 100% acetonitrile over 0–4 mins; Method B: 5% acetonitrile to 100% acetonitrile over 0–8 mins; Method C: 0% acetonitrile to 50% acetonitrile over 0–4 mins). Microwave reactions were performed in a Biotage Initiator+ or CEM Discovery SP instruments. Purification of intermediates and final compounds was performed using silica gel chromatography using the Biotage IsoleraOne flash purification system or unless otherwise noted. All newly synthesized compounds were deemed >95% pure by LCMS (PDA, λ = 200–600 nm).
Synthesis of 2-chloro-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine (3).
1 g of 2,6-dichloro-9H-purine (2) was dissolved in n-BuOH (7 ml) in a screw cap vial. To this diisopropylethylamine (2.0 equiv.) was added followed by addition of 2,2,2-trifluoroethylamine (1.5 equiv.). The reaction mixture was then heated at 90 °C for 16h. The reaction mixture was then allowed to cool down and concentrated under vacuum at 50 °C. Dichloromethane was added and the ppts formed were filtered and checked on LCMS. The first ppts were discarded. The filtrate was then left for 1h. The resulting ppts were filtered and washed with hexane. The solid was dried under high vacuum to yield product (3, yield 17%, light yellow solid, m.p. 244–246). 1H NMR (500 MHz, Acetone-d6) δ 8.15 (s, 1H), 4.43 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 252.03 [M+H]+, tR = 2.19 min (Method A).
General method for preparation of compounds 4a-b.
2-chloro-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine (3) was dissolved in isopropyl alcohol (0.03 M), To this, desired amine (10 equiv.) were added and the reaction mixture was heated at 80 °C for 16h. On completion, reaction was concentrated under vacuum and desired product was purified by preparative HPLC (5–50% water–acetonitrile).
2-(4-methyl-1,4-diazepan-1-yl)-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine (4a).
(Yield: 38%, light brown solid, m.p. 276–278). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.79 (s, 1H), 4.38–4.33 (m, 2H), 4.09 (s, 2H), 3.95–3.92 (m, 2H), 3.38–3.33 (m, 2H), 3.23–3.15 (m, 2H), 2.79 (s, 3H), 2.24–2.17 (m, 2H). LCMS found 330.11 [M+H]+, tR = 2.10 min (Method C).
2-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine (4b).
(Yield: 34%, white solid, m.p. 266–268). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.78 (s, 1H), 4.35–4.31 (m, 2H), 3.89–3.77 (m, 4H), 2.54–2.52 (m, 4H), 2.36 (s, 3H). LCMS found 316.1 [M+H]+, tR = 0.42 min (Method A).
General method for preparation of compounds 4c-l, 4r and 4s.
2-chloro-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine (3) and desired aniline (5 equiv.) were mixed in microwave sealed tube. To this, dioxane (0.02 M) and two drops of HCl (catalytic amount) were added. The reaction mixture was then heated in microwave reactor at 150 °C for 40 mins. The reaction mixture was then basified with NaHCO3 solution. The solid product was filtered and dried under high vacuum to give desired product.
N2-phenyl-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4c).
(Yield: 52%, gray solid, m.p. 338–340). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.33 (s, 1H), 8.56 (brs, 1H), 8.43 (brs, 1H), 7.76 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.27 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 6.94 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 4.41 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 309.02 [M+H]+, tR = 5.73 min (Method B).
N2-(p-tolyl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4d).
(Yield: 47%, light brown solid, m.p. 343–345). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.18 (s, 1H), 8.47 (brs, 1H), 8.32 (brs, 1H), 7.63 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.26 (brs, 1H), 7.08 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 4.50–4.34 (m, 2H), 2.26 (s, 3H). LCMS found 323.06 [M+H]+, tR = 2.33 min (Method A).
N2-(m-tolyl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4e).
(Yield: 57%, off-white solid, m.p. 332–334). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.20 (s, 1H), 8.44 (brs, 1H), 8.31 (brs, 1H), 7.65 (s, 1H), 7.49 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.14 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 6.76 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 4.40 (brs, 2H), 2.29 (s, 3H). LCMS found 323.06 [M+H]+, tR = 2.40 min (Method A).
N2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4f).
(Yield: 50%, brown solid, m.p. 245–247). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.77 (s, 1H), 7.98 (brs, 1H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.67 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 6.83 (d, J = 9.1 Hz, 2H), 4.32 (brs, 2H), 3.72 (s, 3H). LCMS found 339.12 [M+H]+, tR = 2.05 min (Method A).
N2-(3-methoxyphenyl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4g).
(Yield: 56%, brown solid, m.p. 298–300). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ 8.12 (s, 1H), 7.42 (t, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.23–7.15 (m, 2H), 6.65–6.63 (m, 1H), 4.47–4.41 (m, 2H), 3.83 (s, 3H). LCMS found 338.99 [M+H]+, tR = 2.27 min (Method A).
N2-(3-cyanophenyl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4h).
(Yield: 45%, off-white solid, m.p. 294–296). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.66 (s, 1H), 8.58 (s, 1H), 8.43 (s, 2H), 7.92 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.47 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.38–7.07 (m, 2H), 4.39 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 333.96 [M+H]+, tR = 2.42 min (Method A).
N2-(3-chlorophenyl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4i).
(Yield: 54%, gray solid, m.p. 323–325). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.52 (s, 1H), 8.55 (s, 1H), 8.48 (s, 1H), 8.10 (s, 1H), 7.59 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.27 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 6.96 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 4.41 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 343.02 [M+H]+, tR = 2.71 min (Method A).
7-((6-((2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)amino)-9H-purin-2-yl)amino)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one (4j).
(Yield: 24%, off-white solid, m.p. 252–254). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.62 (s, 1H), 9.14 (s, 1H), 8.37 (s, 1H), 8.15 (s, 1H), 7.91 (d, J = 13.8 Hz, 2H), 7.22 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 4.35 (brs, 2H), 3.18 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H), 2.88 (t, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 2.59–2.57 (m, 2H), 2.05–2.02 (m, 2H). LCMS found 377.03 [M+H]+, tR = 2.27 min (Method A).
N2-(4-fluorophenyl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4k).
(Yield: 62%, gray solid, m.p. 326–328). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.33 (s, 1H), 8.55 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.77–7.74 (m, 2H), 7.33–7.26 (m, 2H), 7.13–7.09 (m, 2H), 4.39 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 327.0 [M+H]+, tR = 4.57 min (Method B).
N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-N2-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4l).
(Yield: 49%, gray solid, m.p. 188–190). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.67 (s, 1H), 9.43 (s, 1H), 8.45 (s, 1H), 8.21 (s, 1H), 7.95 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.45 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 4.32 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 377.0 [M+H]+, tR = 2.14 min (Method A).
N2-methyl-N2-phenyl-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4r).
(Yield: 59%, brown solid, m.p. 232–234). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.53 (s, 1H), 7.98 (s, 1H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.37–7.33 (m, 4H), 7.16–7.12 (m, 1H), 4.11 (bs, 2H), 3.46 (s, 3H). LCMS found 323.0 [M+H]+, tR = 2.23 min (Method A).
N2-(pyridin-4-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4s).
(Yield: 36%, off-white semi-solid). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD+CDCl3) δ 9.24 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 6.96 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 4.40–4.34 (m, 2H). LCMS found 309.96 [M+H]+, tR = 1.31 min (Method A).
General method for preparation of compounds 4n-q.
A mixture of 2-chloro-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine (3), respective boronic acid (2 equiv.), cesium carbonate (4 equiv.), and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)-palladium (0) (5 mol%) in 1:2 water/DME (0.02 M) was subjected to heating in microwave at 150 °C for 1h. The reaction mixture was then partitioned thrice with water and dichloromethane. The organic layer was dried and then purified by flash chromatography using 1% to 5% of methanol in dichloromethane gradient to get desired product.
2-phenyl-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine (4n).
(Yield: 26%, off-white solid, m.p. 243–245). 1H NMR (500 MHz, Acetone-d6) δ 8.52 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 8.17 (s, 3H), 7.49 – 7.46 (m, 2H), 4.67 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 294.0 [M+H]+, tR = 2.76 min (Method A).
2-(3-methoxyphenyl)-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine (4o).
(Yield: 42%, light yellow solid, m.p. 267–269). 1H NMR (500 MHz, Acetone-d6) δ 8.18 (s, 1H), 8.10 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 7.39 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.04–7.02 (m, 1H), 4.66 (brs, 2H), 2.86 (s, 3H). LCMS found 324.0 [M+H]+, tR = 2.77 min (Method A).
2-(3-chlorophenyl)-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine (4p).
(Yield: 48%, white solid, m.p. 271–273). 1H NMR (500 MHz, Acetone-d6) δ 8.50 (s, 1H), 8.46 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 8.21 (s, 1H), 7.52–7.50 (m, 2H), 4.67 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 328.0 [M+H]+, tR = 3.09 min (Method A).
2-(4-fluorophenyl)-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine (4q).
(Yield: 34%, off-white solid, m.p. 240–242). 1H NMR (500 MHz, Acetone-d6) δ 8.56 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 8.17 (s, 1H), 7.75–7.70 (m, 1H), 7.64–7.60 (m, 1H), 7.25–7.22 (m, 1H), 4.66 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 312.0 [M+H]+, tR = 2.58 min (Method A).
General method for preparation of compounds 1, 4m and 4t-4ab.
A mixture of 2-chloro-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purin-6-amine (3), respective amine (2 equiv.), Pd2(dba)3 (5 mol%), XPhos (15 mol%) and potassium tert-butoxide (3 equiv.) were added to a reaction vial. To this, t-butanol (0.02 M) was added, reaction vial was flushed with inert gas (nitrogen or argon) and stirred for 16h at 100 °C. The reaction mixture was filtered, and the residue was washed with acetone. The filtrate was dried and then purified by flash chromatography using 1% to 25% of methanol in dichloromethane gradient to get desired product.
N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (1).
(Yield: 59%, light brown solid, m.p. 240–242). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.52 (s, 1H), 9.34 (s, 1H), 8.03 (brs, 1H), 7.89 (s, 1H), 7.59 (s, 1H), 7.38 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.20 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 4.32 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 315.06 [M+H]+, tR = 2.23 min (Method A).
N2-(4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4m).
(Yield: 62%, brown solid, m.p. 255–257). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.50 (s, 1H), 8.69 (s, 1H), 7.95 (s, 1H), 7.84 (s, 1H), 7.61 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.84 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 2H), 4.33 (brs, 2H), 3.04 (t, J = 4.25 Hz, 4H), 2.45 (t, J = 4.55 Hz, 4H), 2.22 (s, 3H). LCMS found 407.19 [M+H]+, tR = 1.27 min (Method A).
N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-N2-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4t).
(Yield: 62%, white solid, m.p. 283–285). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.78 (s, 1H), 9.73 (s, 1H), 9.10 (s, 1H), 8.51 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (s, 1H), 7.76 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 4.33 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 378.0 [M+H]+, tR = 2.71 min (Method A).
N2-(pyrimidin-4-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4u).
(Yield: 29%, off-white solid, m.p. 163–165). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.89 (s, 1H), 9.86 (s, 1H), 8.72 (s, 1H), 8.50 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H), 8.34 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 8.05 (s, 1H), 4.34 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 311.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.38 min (Method A).
N2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4v).
(Yield: 40%, off-white solid, m.p. 328–330). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.89 (s, 1H), 9.53 (s, 1H), 8.53 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H), 8.01 (s, 1H), 6.96 (t, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 4.35 (brs, 2H). LCMS found 311.0 [M+H]+, tR = 1.32 min (Method A).
N2-(4-methylpyrimidin-2-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4w).
(Yield: 28%, off-white solid, m.p. 305–307). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ 8.39 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.95 (s, 1H), 6.88 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 4.48 (brs, 2H), 2.41 (s, 3H). LCMS found 325.0 [M+H]+, tR = 1.43 min (Method A).
N2-(pyrazin-2-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4x).
(Yield: 54%, off-white solid, m.p. 348–350). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.78 (s, 1H), 9.57 (s, 2H), 8.28 (s, 2H), 8.15 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (s, 1H), 4.34 (s, 2H). LCMS found 311.0 [M+H]+, tR = 1.78 min (Method A).
N2-(6-methylpyrazin-2-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4y).
(Yield: 54%, white solid, m.p. >360 out or range). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.77 (s, 1H), 9.42 (s, 2H), 8.26 (s, 1H), 8.05 (s, 1H), 8.00 (s, 1H), 4.32 (brs, 2H), 2.40 (s, 3H). LCMS found 325.0 [M+H]+, tR = 1.92 min (Method A).
N2-(1-ethyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4z).
(Yield: 62%, light orange solid, m.p. 228–230). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.57 (s, 1H), 8.62 (s, 1H), 8.09 (s, 1H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.34 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 6.16 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 4.26 (brs, 2H), 4.00 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.28 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H). LCMS found 327.0 [M+H]+, tR = 1.92 min (Method A).
N2-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4aa).
(Yield: 54%, off-white solid, m.p. 252–254). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.41 (s, 1H), 8.74 (s, 1H), 7.93 (s, 1H), 7.82 (s, 2H), 7.48 (s, 1H), 4.29 (brs, 2H), 3.78 (s, 3H). LCMS found 313.17 [M+H]+, tR = 1.49 min (Method A).
N2-(5,6-dimethyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (4ab).
(Yield: 49%, off-white solid, m.p. 329–331). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.83 (s, 1H), 9.87 (s, 1H), 8.17 (s, 1H), 8.01 (s, 1H), 4.35 (brs, 2H), 2.53 (s, 3H), 2.42 (s, 3H). LCMS found 340.0 [M+H]+, tR = 1.52 min (Method A).
General method for preparation of compounds 5a-e, 5k-5u and 5ac-ae.
2,6-dichloro-9H-purine (1) was dissolved in THF:IPA (1:1; 0.04 M).To this, respective amine (5 equiv.) was added (if amine was in HCl salt form then 7.5 equiv. of triethylamine was added to free base the amine salt), and the reaction mixture was then stirred at 80 °C for 4h. The reaction was set aside for 1h and the ppts formed were filtered to give C-6 aminated intermediate. The C-6 aminated intermediate, 3-aminothiophene (2 equiv.), Pd2(dba)3 (5 mol%), XPhos (15 mol%) and potassium tert-butoxide (3 equiv.) were added to a reaction vial. To this, t-butanol (0.02 M) was added, reaction vial was flushed with inert gas (nitrogen or argon) and stirred for 16h at 100 °C. The reaction mixture was filtered, and the residue was washed with acetone. The filtrate was dried and then purified by flash chromatography using 1% to 25% of methanol in dichloromethane gradient to get desired product.
N6-methyl-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5a).
(Yield: 55%, light brown solid, m.p. 175–177). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.34 (s, 1H), 9.23 (s, 1H), 7.77 (s, 1H), 7.63 (s, 1H), 7.41 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (s, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 4.3 Hz, 1H), 2.96 (s, 3H). LCMS found 247.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.51 min (Method A).
N6-ethyl-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5b).
(Yield: 65%, brown solid, m.p. 196–198). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.31 (s, 1H), 9.16 (s, 1H), 7.75 (s, 1H), 7.59 (s, 1H), 7.39 (s, 1H), 7.35 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 7.16 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, 1H), 3.63–3.37 (m, 2H), 1.19 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H). LCMS found 261.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.71 min (Method A).
N6-propyl-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5c).
(Yield: 52%, brown solid, m.p. 151–153). 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.34 (s, 1H), 9.18 (s, 1H), 7.77 (s, 1H), 7.60 (s, 1H), 7.49 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.35 (s, 1H), 7.17 (d, J = 3.8 Hz, 1H), 1.65–1.60 (m, 2H), 1.20 (m, 2H), 0.91 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 3H). LCMS found 275.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.84 min (Method A).
N6-butyl-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5d).
(Yield: 65%, light brown solid, m.p. 158–160). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.33 (s, 1H), 9.18 (s, 1H), 7.78 (s, 1H), 7.61 (s, 1H), 7.44 (s, 1H), 7.35 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 3.58–3.39 (m, 2H), 1.64–1.58 (m, 2H), 1.37 (dd, J = 14.9, 7.4 Hz, 2H), 0.93 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H). LCMS found 289.06 [M+H]+, tR = 1.91 min (Method A).
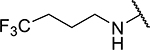
N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-N6-(4,4,4-trifluorobutyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5e).
(Yield: 47%, brown solid, m.p. 145–147). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.17 (s, 1H), 7.80 (s, 1H), 7.59 (s, 2H), 7.34 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.17 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 3.58 (dd, J = 34.1, 18.8 Hz, 2H), 2.39–2.27 (m, 2H), 1.90–1.80 (m, 2H). LCMS found 343.1 [M+H]+, tR = 2.15 min (Method A).
6-(4,4-difluoropiperidin-1-yl)-N-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purin-2-amine (5k).
(Yield: 73%, light brown solid, m.p. 209–211). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.57 (s, 1H), 9.31 (s, 1H), 7.88 (s, 1H), 7.52 (s, 1H), 7.38 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 7.17 (dd, J = 5.1, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 4.55 – 4.17 (m, 4H), 2.15 – 2.03 (m, 4H). LCMS found 337.11 [M+H]+, tR = 2.65 min (Method A).
N-(thiophen-3-yl)-6-(4-(trifluoromethyl)piperidin-1-yl)-9H-purin-2-amine (5l).
(Yield: 72%, light yellow solid, m.p. 139–141). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.53 (s, 1H), 9.26 (s, 1H), 7.85 (s, 1H), 7.52 (s, 1H), 7.38 (dd, J = 5.2, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.17 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H), 5.55–5.44 (m, 1H), 3.08 (t, J = 12.3 Hz, 2H), 2.74–2.70 (m, 1H), 2.10–1.94 (m, 3H), 1–51-1.42 (m, 2H). LCMS found 369.17 [M+H]+, tR = 2.70 min (Method A).
6-(azetidin-1-yl)-N-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purin-2-amine (5m).
(Yield: 72%, brown solid, m.p. 173–175). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.37 (s, 1H), 9.28 (s, 1H), 7.78 (s, 1H), 7.61 (d, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.17 (dd, J = 5.1, 0.7 Hz, 1H), 4.51 – 4.11 (m, 4H), 2.47 – 2.38 (m, 2H). LCMS found 273.06 [M+H]+, tR = 1.57 min (Method A).
N6-cyclohexyl-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5n).
(Yield: 70%, brown solid, m.p. 177–179). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.16 (s, 1H), 7.78 (s, 1H), 7.59 (s, 1H), 7.35 (dd, J = 4.9, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 4.5 Hz, 2H), 4.14–4.04 (m, 1H), 1.99–1.94 (m, 2H), 1.80 – 1.75 (m, 2H), 1.67–1.64 (m, 1H), 1.39 – 1.30 (m, 3H), 1.25–1.16 (m, 2H). LCMS found 315.14 [M+H]+, tR = 2.08 min (Method A).
N6-isopropyl-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5o).
(Yield: 59%, brown solid, m.p. 132–134). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.34 (s, 1H), 9.17 (s, 1H), 7.78 (s, 1H), 7.61 (s, 1H), 7.35 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, 1H), 7.14 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H), 3.18 (m, 1H), 1.25 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 6H). LCMS found 275.08 [M+H]+, tR = 1.82 min (Method A).
N6,N6-diethyl-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5p).
(Yield: 77%, light brown solid, m.p. 88–90). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.39 (s, 1H), 9.14 (s, 1H), 7.80 (s, 1H), 7.53 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.36 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 3.96 (brs, 4H), 1.22 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 6H). LCMS found 289.06 [M+H]+, tR = 1.89 min (Method A).
N6-cyclopropyl-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5q).
(Yield: 70%, light brown solid, m.p. 130–132). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.22 (s, 1H), 7.79 (s, 1H), 7.75 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.34 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 1.25–1.15 (m, 2H), 0.90–0.64 (m, 3H). LCMS found 273.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.17 min (Method A).
N6-(tert-butyl)-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5r).
(Yield: 59%, brown solid, m.p. 150–152). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.14 (s, 1H), 7.77 (s, 1H), 7.59 (s, 1H), 7.38 – 7.32 (m, 1H), 7.20 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 6.25 (s, 1H), 1.53 (s, 9H). LCMS found 289.2 [M+H]+, tR = 1.82 min (Method A).
N6-isobutyl-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5s).
(Yield: 21%, off-white semi-solid). 1H NMR (500 MHz, Acetone-d6) δ 11.42 (s, 1H), 8.46 (s, 1H), 7.74 (d, J = 3.9 Hz, 2H), 7.33 – 7.27 (m, 1H), 7.23 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (brs, 1H), 3.50–3.43 (m, 1H), 2.88 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 2H), 0.99 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 6H). LCMS found 289.06 [M+H]+, tR = 1.87 min (Method A).
N6-cyclopentyl-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5t).
(Yield: 80%, light brown solid, m.p. 126–128). 1H NMR (500 MHz, Acetone-d6) δ 11.40 (s, 1H), 8.46 (s, 1H), 7.74 (s, 2H), 7.26 (d, J = 18.1 Hz, 2H), 6.37 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 1H), 4.58 (s, 1H), 1.99 – 1.47 (m, 7H). LCMS found 301.08 [M+H]+, tR = 1.93 min (Method A).
N6-(2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethyl)-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5u).
(Yield: 51%, light orange solid, m.p. 162–164). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.32 (s, 1H), 9.17 (s, 1H), 7.76 (s, 1H), 7.61 (s, 1H), 7.32 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (s, 1H), 7.16 (t, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 3.69 – 3.49 (m, 2H), 3.15 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 2.66 (t, J = 6.7 Hz, 2H), 1.72–1.62 (m, 4H). *three aliphatic protons merged with DMSO signal. LCMS found 330.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.11 min (Method A).
N2-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-N6-(4,4,4-trifluorobutyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5ac).
(Yield: 37%, off-white solid, m.p. 275–277). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.28 (s, 1H), 8.58 (brs, 1H), 8.24 (s, 1H), 7.84 (s, 1H), 7.52 (s, 1H), 3.80 (s, 3H), 3.65 – 3.51 (m, 2H), 2.45 – 2.37 (m, 2H), 1.92 – 1.81 (m, 2H). LCMS found 341.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.61 min (Method A).
N2-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-N6-(2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5ad).
(Yield: 48%, brown solid, m.p. 128–130). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.26 (s, 1H), 8.59 (s, 1H), 7.87 (s, 1H), 7.72 (s, 1H), 7.46 (s, 1H), 7.15 (s, 1H), 3.77 (s, 3H), 3.67 – 3.50 (m, 3H), 2.69 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H), 2.57 – 2.53 (m, 3H), 1.75 – 1.67 (m, 4H). LCMS found 328.23 [M+H]+, tR = 1.49 min (Method A).
N6-butyl-N2-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5ae).
(Yield: 51%, off-white solid, m.p. 205–207). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.89 (s, 1H), 7.73 (s, 1H), 7.57 (s, 1H), 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.57 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.67 (dd, J = 14.6, 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.47 (dd, J = 15.0, 7.4 Hz, 2H), 0.99 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H). LCMS found 287.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.47 min (Method A).
General method for preparation of compounds 5f-j and 5ab.
2,6-dichloro-9H-purine (1) was dissolved in THF (0.04 M). To this, respective amine (10 equiv.) was added and the reaction mixture was then stirred at room temp. for 16h. The reaction was set aside for 1h and the ppts formed were filtered to give C-6 aminated intermediate. The C-6 aminated intermediate, 3-aminothiophene (2 equiv.), Pd2(dba)3 (5 mol%), XPhos (15 mol%) and potassium tert-butoxide (3 equiv.) were added to a reaction vial. To this, t-butanol (0.02 M) was added, reaction vial was flushed with inert gas (nitrogen or argon) and stirred for 16h at 100 °C. The reaction mixture was filtered, and the residue was washed with acetone. The filtrate was dried and then purified by flash chromatography using 1% to 25% of methanol in dichloromethane gradient to get desired product.
6-morpholino-N-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purin-2-amine (5f).
(Yield: 52%, light yellow solid, m.p. 250–252). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.52 (s, 1H), 9.25 (s, 1H), 7.85 (s, 1H), 7.51 (s, 1H), 7.37 (dd, J = 4.9, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.16 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 4.30–4.10 (m, 4H), 3.76–3.70 (m, 4H). LCMS found 303.0 [M+H]+, tR = 1.89 min (Method A).
6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-N-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purin-2-amine (5g).
(Yield: 61%, light brown solid, m.p. 152–154). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.49 (s, 1H), 9.22 (s, 1H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.51 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.37 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 7.16 (dd, J = 5.0, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 4.32–4.08 (m, 4H), 2.45–2.41 (m, 4H), 2.23 (s, 3H). LCMS found 316.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.28 min (Method A).
6-(piperidin-1-yl)-N-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purin-2-amine (5h).
(Yield: 59%, brown solid, m.p. 180–182). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.44 (s, 1H), 9.17 (s, 1H), 7.80 (s, 1H), 7.51 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.36 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 7.17 (dd, J = 5.1, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 4.23–4.08 (m, 4H), 3.18 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H), 1.69–1.59 (m, 4H). LCMS found 301.0 [M+H]+, tR = 2.19 min (Method A).
6-(pyrrolodin-1-yl)-N-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purin-2-amine (5i).
(Yield: 71%, light brown solid, m.p. 208–210). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.35 (s, 1H), 9.17 (s, 1H), 7.77 (s, 1H), 7.60 (dd, J = 3.2, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.35 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (dd, J = 5.1, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 4.11–4.04 (dd, J = 28.2, 8.4 Hz, 3H), 3.18 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H), 2.02 – 1.93 (m, 4H). LCMS found 287.0 [M+H]+, tR = 1.75 min (Method A).
6-(4-methyl-1,4-diazepan-1-yl)-N-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purin-2-amine (5j).
(Yield: 62%, brown solid, m.p. 144–146). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.43 (s, 1H), 9.18 (s, 1H), 7.80 (s, 1H), 7.52 (s, 1H), 7.36 (dd, J = 4.9, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H), 4.61–4.28 (m, 2H), 3.88 (dd, J = 39.9, 22.5 Hz, 2H), 2.83 – 2.55 (m, 3H), 2.28 (s, 3H), 2.10 – 1.78 (m, 3H). LCMS found 330.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.21 min (Method A).
N-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-6-morpholino-9H-purin-2-amine (5ab).
(Yield: 45%, light orange solid, m.p. 261–263). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 12.38 (s, 1H), 8.61 (s, 1H), 7.75 (s, 2H), 7.43 (s, 1H), 4.21 – 4.02 (m, 4H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 3.71 – 3.67 (m, 4H). LCMS found 301.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.42 min (Method A).
Synthesis of N2-(4-fluorophenyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (5aa).
100 mg of 2,6-dichloro-9H-purine (2) was dissolved 15 ml on ammonium hydroxide (1N sol in MeOH) and heated in microwave reactor at 120 °C for 90 mins. The precipitates formed were filtered and washed with 2 ml of methanol and dried to give 2-chloro-9H-purin-6-amine. The 2-chloro-9H-purin-6-amine was then added to vial containing 4-fluoroaniline (1.5 equiv.), Pd2(dba)3 (2 mol%), RuPhos (5 mol%) and potassium carbonate (3 equiv.). To this, t-butanol (0.02 M) was added, reaction vial was flushed with inert gas (nitrogen or argon) and heated in microwave at 180 °C for 2h. The reaction mixture was then diluted with dichloromethane:methanol (1:1) and filtered. The filtrate was dried and purified by preparative HPLC (5–50% water–acetonitrile) to give desired product 5aa (yield 17%, white solid, m.p. 214–216). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ ppm 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.70–7.68 (m, 2H), 7.02–6.99 (m, 2H). LCMS found 244.98 [M+H]+, tR = 2.33 min (Method A).
General method for preparation of compounds 5v-z.
2,6-dichloro-9H-purine (1) was dissolved in THF (0.04 M). To this, respective amine (10 equiv.) was added and the reaction mixture was then stirred at room temp. for 16h. The reaction was set aside for 1h and the ppts formed were filtered to give C-6 aminated intermediate. The C-6 aminated intermediate, and aniline (5 equiv.) were mixed in microwave sealed tube. To this, dioxane (0.02 M) and two drops of HCl (catalytic amount) were added. The reaction mixture was then heated in microwave reactor at 150 °C for 40 mins. The reaction mixture was then basified with NaHCO3 solution. The solid product was filtered and dried under high vacuum to give desired product.
6-morpholino-N-phenyl-9H-purine-2-amine (5v).
(Yield: 59%, brown solid, m.p. 263–265). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.09 (s, 1H), 7.69 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.51–7.29 (m, 4H), 6.98 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.26–4.16 (m, 2H), 3.79 – 3.74 (m, 4H), 3.10 – 3.06 (m, 2H). LCMS found 297.1 [M+H]+, tR = 2.03 min (Method A).
6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-N-phenyl-9H-purine-2-amine (5w).
(Yield: 54%, gray solid, m.p. 110–112). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 7.99 (s, 1H), 7.74 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.50–7.25 (m, 5H), 6.90 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 3.64–3.54 (m, 5H), 3.18–3.12 (m, 2H), 2.82 – 2.77 (m, 1H), 2.77 (s, 3H). LCMS found 310.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.28 min (Method A).
N-phenyl-6-(piperidin-1-yl)-9H-purin-2-amine (5x).
(Yield: 28%, light brown solid, m.p. 196–198). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.27 (s, 1H), 7.99 (s, 1H), 7.71 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.28 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 6.95 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.27 – 4.07 (m, 4H), 1.74 – 1.66 (m, 2H), 1.63–1.59 (m, 4H). LCMS found 295.1 [M+H]+, tR = 2.22 min (Method A).
N-phenyl-6-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)-9H-purin-2-amine (5y).
(Yield: 68%, gray solid, m.p. 218–220). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.21 (s, 1H), 7.75 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.43 – 7.41 (m, 2H), 7.35 – 7.25 (m, 2H), 7.03 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 4.12 – 3.99 (m, 2H), 3.82 – 3.72 (m, 2H), 2.09 – 1.95 (m, 4H). LCMS found 281.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.78 min (Method A).
6-(4-methyl-1,4-diazepan-1-yl)-N-phenyl-9H-purine-2-amine (5z).
(Yield: 56%, brown solid, m.p. 222–224). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 10.75 (s, 1H), 7.98 (s, 1H), 7.76 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.45 – 7.25 (m, 3H), 6.91 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 3.66 – 3.59 (m, 2H), 3.50 – 3.42 (m, 2H), 3.36 – 3.18 (m, 4H), 2.79 (s, 3H), 2.43 – 2.37 (m, 1H), 2.24 – 2.20 (m, 1H). LCMS found 324.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.28 min (Method A).
General method for preparation of compounds 9–11 and 13a.
Desired dichloro-scaffold (1 equiv.) was dissolved in n-BuOH (0.03 M) in a screw cap vial. To this diisopropylethylamine (2.0 equiv.) was added followed by addition of 2,2,2-trifluoroethylamine (1.5 equiv.). The reaction mixture was then heated at 90 °C for 16h. The reaction mixture was then allowed to cool down and concentrated under vacuum at 50 °C to an oily mass. To this, water was added and ppts formed were filtered, washed with water and dried to give 2-chloro-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-substituted intermediate. The 2-chloro-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-substituted intermediate was then added to the reaction vial containing desired amine (2 equiv.), Pd2(dba)3 (5 mol%), XPhos (15 mol%) and potassium tert-butoxide (3 equiv.). To this, t-butanol (0.02 M) was added, reaction vial was flushed with inert gas (nitrogen or argon) and stirred for 16h at 100 °C. The reaction mixture was filtered, and the residue was washed with acetone. The filtrate was dried and then purified by flash chromatography using 1% to 25% of methanol in dichloromethane gradient to get desired product.
9-methyl-N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (9a).
(Yield: 34%, light yellow solid, m.p. 195–197). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.47 (s, 1H), 8.07 (s, 1H), 7.89 (s, 1H), 7.68 (s, 1H), 7.37 (dd, J = 4.9, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.19 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, 1H), 4.31 (brs, 2H), 3.68 (s, 3H). LCMS found 329.1 [M+H]+, tR = 2.80 min (Method A).
9-methyl-N2-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-N6-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-purine-2,6-diamine (9b).
(Yield: 33%, light orange solid, m.p. 235–237). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 8.92 (s, 1H), 7.98 (s, 2H), 7.83 (s, 1H), 7.50 (s, 1H), 4.29 (brs, 2H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 3.66 (s, 3H). LCMS found 327.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.99 min (Method A).
N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-N4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine-2,4-diamine (10).
(Yield: 43%, light yellow solid, m.p. 182–184). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.48 (s, 1H), 8.24 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 1H), 8.04 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (s, 1H), 7.38 (dd, J = 5.1, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 7.21 (dd, J = 8.6, 5.2 Hz, 2H), 4.41 – 4.33 (m, 2H). LCMS found 331.0 [M+H]+, tR = 1.99 min (Method A).
N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-N4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)quinazoline-2,4-diamine (11).
(Yield: 42%, light brown solid, m.p. 123–125). 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.54 (s, 1H), 8.53 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H), 8.12 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.83 (brs, 1H), 7.64 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.50 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.40 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 7.24 – 7.21 (m, 2H), 4.49 – 4.37 (m, 2H). LCMS found 325.01 [M+H]+, tR = 1.78 min (Method A).
N2-(thiophen-3-yl)-N4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine (13a).
(Yield: 30%, brown solid, m.p. 85–87). 1H NMR (500 MHz, Acetone-d6) δ 8.67 (s, 1H), 7.99 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H), 7.68 (s, 1H), 7.34 (dd, J = 5.2, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 7.29 – 7.26 (m, 1H), 6.95 (s, 1H), 6.16 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H), 4.33 – 4.28 (m, 2H). LCMS found 275.08 [M+H]+, tR = 1.59 min (Method A).
Synthesis of N2-phenyl-N4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine (13b).
2,4-dichloropyrimidine (1 equiv.) was dissolved in n-BuOH (0.03 M) in a screw cap vial. To this diisopropylethylamine (2.0 equiv.) was added followed by addition of 2,2,2-trifluoroethylamine (1.5 equiv.). The reaction mixture was then heated at 90 °C for 16h. The reaction mixture was then allowed to cool down and concentrated under vacuum at 50 °C to an oily mass. To this, water was added and ppts formed were filtered, washed with water and dried to give intermediate 2-chloro-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)pyrimidin-4-amine. The intermediate and aniline (5 equiv.) were mixed in microwave sealed tube. To this, dioxane (0.02 M) and two drops of HCl (catalytic amount) were added. The reaction mixture was then heated in microwave reactor at 150 °C for 40 mins. The reaction mixture was then basified with NaHCO3 solution. The solid product was filtered and dried under high vacuum to give desired product (13b, yield: 30%, off-white solid, m.p. 253–255). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.76 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H), 7.50 – 7.46 (m, 4H), 7.36 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.35 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 4.31 – 4.25 (m, 2H). LCMS found 269.1 [M+H]+, tR = 1.69 min (Method A).
Strains and media.
Bloodstream Trypanosoma brucei brucei Lister 427 (STIB 795) was cultured in Hirumi’s modified Iscove’s medium (HMI-9), supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS, at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in T-25 vented flask (Corning®). MRC5-SV2 cell line (SV40-transformed human lung fibroblast cell line) was cultured in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in T-75 vented flask (Corning®). The assays were run in sterile 96-well transparent Nunclon plates.
Preparation of compound plates.
For dose-response experiments, compound plates were prepared for each analogue by serial 3-fold dilutions in 100% DMSO. Five concentration points (mammalian cytotoxicity) or ten concentration points (parasite growth inhibition), were made in 96-well transparent Nunclon plates, and plates were stored sealed at −20 °C for no more than four weeks.
Growth inhibition assay for T. brucei brucei.
4 μL per well from compound master plates were dispensed into a new plate and 96 μL of HMI-9 per well were added to generate a 4% DMSO intermediate plate. Cultures of T. b. brucei in logarithmic phase were diluted to a working cell density of 2,750 cells/mL and 90 μL/well dispensed into 96-well flat-bottom transparent assay plates (Nunc®). 10 μL/well from intermediate plates were added so final cell concentration was 2,500 cell/mL, and final top concentration of compounds was 40 μM in 0.4% DMSO per well. Assay plates were incubated for 72 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. After 68 hours of incubation, 20 μL of a 440 μM resazurin solution in pre-warmed HMI-9 was added to each well and incubated for another 4 h. Fluorescence was then measured in an Infinite F200 plate reader (Tecan®) at 550 nm (excitation filter) and 590 nm (emission filter). A four-parameter equation was employed to fit the dose-response curves and determine EC50 using the SigmaPlot® 13.0 software. Assays were performed in duplicate at least twice, to achieve a minimal n=4 per dose response, and pentamidine was routinely included in compound plates as internal quality control.
Cytotoxicity assay in MRC5 cells.
Fresh intermediate plates were made as described, adding 95 μL of DMEM complete media to 5 μL of compound per well setting a 5% DMSO amount. Log-phase MRC5 cells were removed from a T-75 TC flask using TrypLE® Express (Thermo®) and dispersed by gentle pipetting. Cell density was adjusted to working concentration in prewarmed DMEM medium: 25,000 cells in 90 μL of culture were plated in 96-well transparent Nunclon plates and let to settle for 24 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. After settling incubation, 10 μL of freshly made intermediate plate were added per well: final maximal concentration for compounds was 50 μM in 0.5% DMSO per well. Plates were incubated for 48 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. At 4 h prior to fluorescence measurement, 20 μL of 500 μM resazurin solution was added. Fluorescence was read in an Infinite F200 plate reader (Tecan®) at 550 nm (excitation filter) and 590 nm (emission filter). A four-parameter equation was used to fit the dose-response curves and determination of EC50 by SigmaPlot ® 13.0 software. Assays were performed in duplicate at least twice for positive compounds, to achieve a minimal n=3 per dose response.
Pharmacokinetics Protocols.
Compound was administered intraperitoneally (ip) to two groups of female NMRI mice (group 1, n = 3; group 2, n = 6) supplied by Charles River (Germany) Ltd. The compound was prepared in 1% (v/v) DMSO/99% (v/v) 20% (w/v) sulfobutyl ether–β-cyclodextrin (SBEβ-CD)/Captisol, used as a solubilizing agent) in water, and the dosing volume was 10 mL/kg for a total dose of 10 mg/kg. Food and tap water were available ad libitum. Following ip dosing, blood samples were collected from the tail vein into capillary tubes containing K2EDTA at the following time points: 0.0833, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 24 h. In order to obtain simultaneous blood and brain samples, group 2 mice were placed under terminal anesthetic (isoflurane), and blood samples (0.3 mL) were collected from the retro-orbital sinus into K2EDTA tubes at 0.5 h (n = 3) and 4 h (n = 3) after compound administration. Immediately following blood sample collection, death was confirmed by cervical dislocation, and the brain removed. Aliquots of each blood sample were diluted in an equal volume of water. Mouse brain samples were weighed, water was added at a 1/2 (w/v) ratio (brain/water), and then samples were homogenized. Both blood and brain samples were stored −80 °C until analysis. For PK analysis of ABT-pretreated animals, blood samples from treated mice (infected and non-infected) were taken at 0.5, 2, 4 and 6 h of treatment on day 1 of treatment; and at 0.5 h of day 5 of treatment. Diluted blood and brain homogenates were processed under standard liquid–liquid extraction procedures using CAN containing an internal standard (nifedipine) and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Noncompartmental analysis was performed using the Phoenix pharmacokinetic software, version 1.4 (Certara), and Cmax, tmax, AUClast, AUC, and t1/2 were estimated.
Blood-stage efficacy model.
All procedures were performed in the Institute of Parasitology and Biomedicine Lopez-Neyra (Spanish National Research Council, CSIC) and approved according with the European and Spanish ethical regulations. Infection was carried out in female NMRI mice (Charles River Laboratories) by i.p. injection of 104 bloodstream forms of T. brucei brucei (STIB795) in 0.2 mL TDB glucose from a cryopreserved stock. Three days later, infected animals with confirmed parasitemia were distributed into two groups: control (infected mice treated with vehicle (4 % DMSO, 20 % Captisol®), n=3) and treated (infected mice treated with 30 mg/kg/day of 4aa, n=3). An additional group was used for PK analysis (non-infected mice treated with 30 mg/kg/day of 4aa, n=3). All mice received a 0.2 mL i.p. injection at day 3 from infection during 5 consecutive days. Pre-treatment with 50 mg/kg/day ABT (1-Aminobenzotriazole, Sigma-Aldrich), a known inhibitor of CYP enzymes, 1 h prior compound injection was administered. Blood samples from tail tip were mixed with sterile water (ratio 1:2). To eliminate the risk of infections, the samples undergo 3 freeze-thaw cycles. Parasitemia was periodically examined, diluting 2 μL of blood from infected mice tail in 100 μL of TDB glucose and counting in a Neubauer chamber in a light microscope, and the day of death was recorded.
Supplementary Material
Figure 1.
Structure of NEU-1106 (1) and our medicinal chemistry strategy
Acknowledgments and Notes
We are grateful to David Swinney (iRND3, for TbMAPK6 experiment), AstraZeneca (for in vitro ADME experiments), Charles River Lab (for cell permeability, mouse liver microsome stability, and CYP enzyme studies) and GlaxoSmithKline (for in vivo pharmacokinetics experiments). This work was supported by the Tres Cantos Open Lab Foundation and National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (R01AI114685; R01AI126311; R01AI124046 and R01AI104576). All animal studies were ethically reviewed and carried out in accordance with Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986; and the CSIC and GSK Policy on the Care, Welfare and Treatment of Animals. We certify that the research using each of the HBS marked above was conducted according to the requirements of POL-GSKF-410 and associated relevant SOPs, and that all related documentation is stored in an approved HBSM database.
Abbreviations.
- HAT
Human African trypanosomiasis
- ADME
absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion
- NTDs
Neglected tropical diseases
- SAR
structure activity relationship
- SPR
structure property relationship
- PPB
plasma protein binding
- CNS
central nervous system
- MPO
multiparameter optimization
- PSA
polar surface area
- LLE
lipophilic ligand efficiency
- HLM
human liver microsome
- CLint
intrinsic clearance
- Aq. sol.
thermodynamic aqueous solubility
- DIPEA
N,N-diisopropylethylamine
- TbMAPK6
T. brucei mitogen-activated protein kinase 6
- PK
pharmacokinetics
- ABT
1-aminobenzotriazole
- IP
intraperitoneal
- AAT
African animal trypanosomiasis
- AUC
area under the curve
Footnotes
ASSOCIATED CONTENT
Supporting Information. Supplemental biological (TbMAPK6 and human kinase), PK and ADME data (annotated with NEU registry numbers), experiment protocols and HPLC traces of all compounds tested. Compound ID numbers and their associated SMILES strings.
REFERENCES
- 1.World Health Organization: neglected tropical diseases. https://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/diseases/en/ (accessed May 13, 2019).
- 2.Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative: about sleeping sickness. https://www.dndi.org/diseases-projects/hat/ (accessed May 13, 2019).
- 3.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: parasites - African trypanosomiasis. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/sleepingsickness/epi.html (accessed April 7, 2020).
- 4.WHO outlines criteria to assess elimination of sleeping sickness. https://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/news/criteria-eliminate-sleeping-sickness/en/ (accessed May 27, 2020).
- 5.Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative: about sleeping sickness, disease background. https://www.dndi.org/diseases-projects/hat/hat-disease-background/ (accessed May 27, 2020).
- 6.Rijo-Ferreira F; Carvalho T; Afonso C; Sanches-Vaz M; Costa RM; Figueiredo LM; Takahashi JS Sleeping sickness is a circadian disorder. Nat. Commun 2018, 9, 62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Klug DM; Gelb MH; Pollastri MP Repurposing strategies for tropical disease drug discovery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2016, 26, 2569–2576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Deeks ED Fexinidazole: first global approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 215–220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.World Health Organization: Human African trypanosomiasis-research https://www.who.int/trypanosomiasis_african/research/en/ (accessed April 7, 2020).
- 10.Benz C; Thomas E; Hammarton TC Trypanosomatid Cell Division Kinases. In Protein Phosphorylation in Parasites, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: 2013; pp 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Merritt C; Silva LE; Tanner AL; Stuart K; Pollastri MP Kinases as druggable targets in trypanosomatid protozoan parasites. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11280–11304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Urbaniak MD; Mathieson T; Bantscheff M; Eberhard D; Grimaldi R; Miranda-Saavedra D; Wyatt P; Ferguson MA; Frearson J; Drewes G Chemical proteomic analysis reveals the drugability of the kinome of Trypanosoma brucei. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1858–1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bachovchin KA; Sharma A; Bag S; Klug DM; Schneider KM; Singh B; Jalani HB; Buskes MJ; Mehta N; Tanghe S; Momper JD; Sciotti RJ; Rodriguez A; Mensa-Wilmot K; Pollastri MP; Ferrins L Improvement of aqueous solubility of lapatinib-derived analogues: identification of a quinolinimine lead for human african trypanosomiasis drug development. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 665–687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Devine W; Woodring JL; Swaminathan U; Amata E; Patel G; Erath J; Roncal NE; Lee PJ; Leed SE; Rodriguez A; Mensa-Wilmot K; Sciotti RJ; Pollastri MP Protozoan parasite growth inhibitors discovered by cross-screening yield potent scaffolds for lead discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 5522–5537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Patel G; Karver CE; Behera R; Guyett PJ; Sullenberger C; Edwards P; Roncal NE; Mensa-Wilmot K; Pollastri MP Kinase scaffold repurposing for neglected disease drug discovery: discovery of an efficacious, lapatinib-derived lead compound for trypanosomiasis. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3820–3832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Woodring JL; Behera R; Sharma A; Wiedeman J; Patel G; Singh B; Guyett P; Amata E; Erath J; Roncal N; Penn E; Leed SE; Rodriguez A; Sciotti RJ; Mensa-Wilmot K; Pollastri MP Series of alkynyl-substituted thienopyrimidines as inhibitors of protozoan parasite proliferation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett 2018, 9, 996–1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Singh B; Bernatchez JA; McCall LI; Calvet CM; Ackermann J; Souza JM; Thomas D; Silva EM; Bachovchin KA; Klug DM; Jalani HB; Bag S; Buskes MJ; Leed SE; Roncal NE; Penn EC; Erath J; Rodriguez A; Sciotti RJ; Campbell RF; McKerrow J; Siqueira-Neto JL; Ferrins L; Pollastri MP Scaffold and parasite hopping: discovery of new protozoal proliferation inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett 2020, 11, 249–257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Diaz R; Luengo-Arratta SA; Seixas JD; Amata E; Devine W; Cordon-Obras C; Rojas-Barros DI; Jimenez E; Ortega F; Crouch S; Colmenarejo G; Fiandor JM; Martin JJ; Berlanga M; Gonzalez S; Manzano P; Navarro M; Pollastri MP Identification and characterization of hundreds of potent and selective inhibitors of Trypanosoma brucei growth from a kinase-targeted library screening campaign. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gramec D; Peterlin Masic L; Sollner Dolenc M Bioactivation potential of thiophene-containing drugs. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 1344–1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hopkins AL; Keseru GM; Leeson PD; Rees DC; Reynolds CH The role of ligand efficiency metrics in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 105–121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hughes JD; Blagg J; Price DA; Bailey S; Decrescenzo GA; Devraj RV; Ellsworth E; Fobian YM; Gibbs ME; Gilles RW; Greene N; Huang E; Krieger-Burke T; Loesel J; Wager T; Whiteley L; Zhang Y Physiochemical drug properties associated with in vivo toxicological outcomes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4872–4875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Baumeister S; Schepmann D; Wunsch B Synthesis and receptor binding of thiophene bioisosteres of potent GluN2B ligands with a benzo[7]annulene-scaffold. Medchemcomm 2019, 10, 315–325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhao Y; Lee MH; Paderu P; Lee A; Jimenez-Ortigosa C; Park S; Mansbach RS; Shaw KJ; Perlin DS Significantly improved pharmacokinetics enhances in vivo efficacy of APX001 against echinocandin- and multidrug-resistant candida isolates in a mouse model of invasive candidiasis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00425–18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mico BA; Federowicz DA; Ripple MG; Kerns W In vivo inhibition of oxidative drug metabolism by, and acute toxicity of, 1-aminobenzotriazole (ABT). A tool for biochemical toxicology. Biochem. Pharmacol 1988, 37, 2515–2519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.