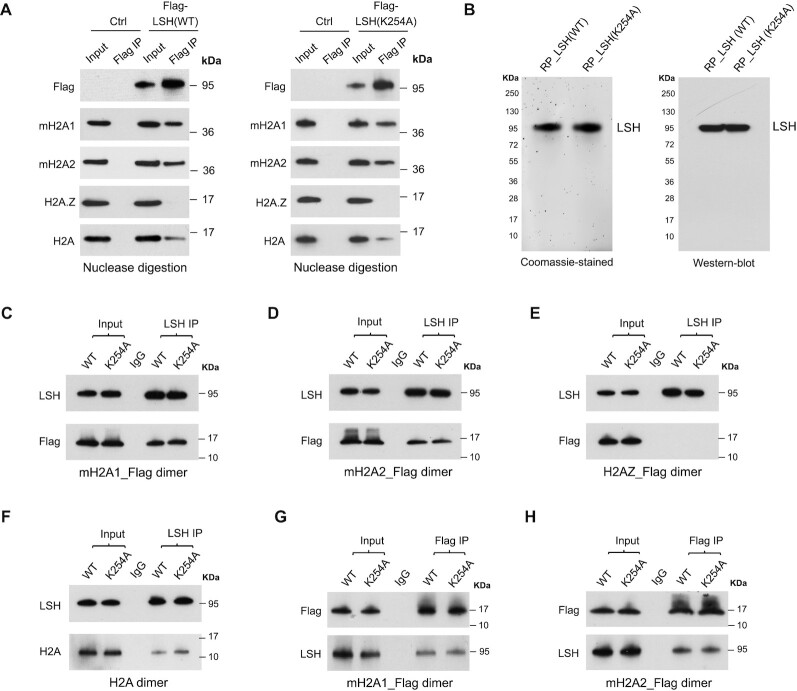
Figure 1.
Characterization of LSH and mH2A interaction. (A) Flag-IP of mH2A1, mH2A2, H2A.Z and H2A confirmed by Western-blot analysis in U2OS cells with stable expression of Flag-LSH (WT) or Flag-LSH (K254A) fusion protein. Cells without fusion protein expression were used as controls (Ctrl). Cell lysates were collected and treated with universal nuclease to remove genomic DNA for subsequent Co-IP. (B) Coomassie-stained gel of purified recombinant WT and K254A mutant LSH proteins (left panel), and Western-blot analysis with LSH antibody (right panel). RP, recombinant protein. (C–F) Western-blot analysis of purified LSH (WT) or LSH (K254A) recombinant protein Co-IP with mH2A1_Flag–H2B dimer (C), mH2A2_Flag–H2B dimer (D), H2AZ_Flag-H2B dimer (E) or H2A–H2B dimer (F) in vitro. IP was performed using beads coupled with LSH antibody or control IgG. (G-H) Western-blot analysis of mH2A1_Flag-H2B dimer (G) or mH2A2_Flag-H2B dimer (H) Co-IP with recombinant WT or K254A mutant LSH protein in vitro. IP was performed using beads coupled with Flag antibody or control IgG.