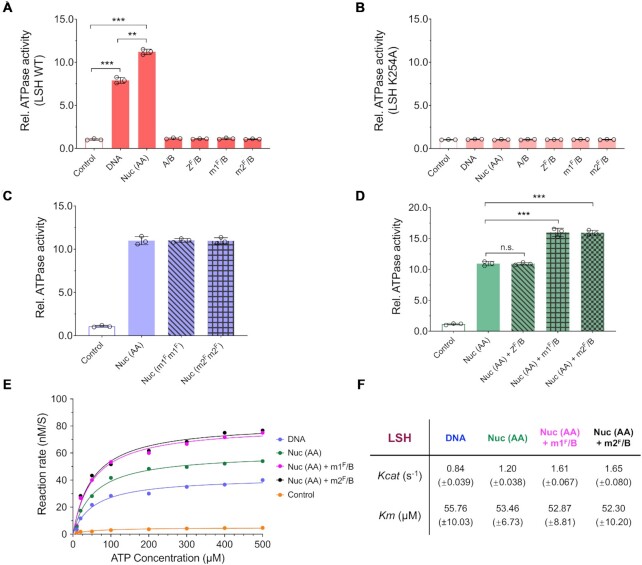
Figure 5.
Stimulation of ATPase activity by nucleosome and mH2A–H2B dimer. (A, B) ATPase activity assay of LSH (WT, A) or LSH mutant (K254A, B) recombinant protein with addition of DNA, H2A containing mono-nucleosome (Nuc (AA)), H2A–H2B dimer (A/B), H2AZ_Flag–H2B dimer (ZF/B), mH2A1_Flag–H2B dimer (m1F/B) or mH2A2_Flag–H2B dimer (m2F/B). Reactions without cofactors served as controls. ** P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001. (C) Comparisons of ATPase activity of LSH with addition of Nuc (AA), or nucleosomes reconstituted with mH2A1_Flag (Nuc (m1Fm1F)) or with mH2A2_Flag (Nuc (m2Fm2F)). Samples without cofactors served as controls. (D) Comparisons of ATPase activity of LSH by addition of Nuc (AA) alone, or in combination with free histone dimers ZF/B, m1F/B or m2F/B. *** P < 0.001 and n.s. means not significant. (E, F) Kinetic analysis of LSH’s ATPase activity with addition of DNA or Nuc (AA) alone, or combination of Nuc (AA) with m1F/B or m2F/B (E). The kinetic parameters were determined by nonlinear fitting of the Michaelis-Menten curve over plotted values. Turnover number of Kcat (obtained from dividing maximal velocity by total enzyme concentration, s–1) and Km (ATP concentration at half maximal velocity, μM) were shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments with individual enzyme preparations (F). Samples were incubated with different ATP concentration ranging from 10 to 500 μM for 30 min. Samples without cofactors served as controls.