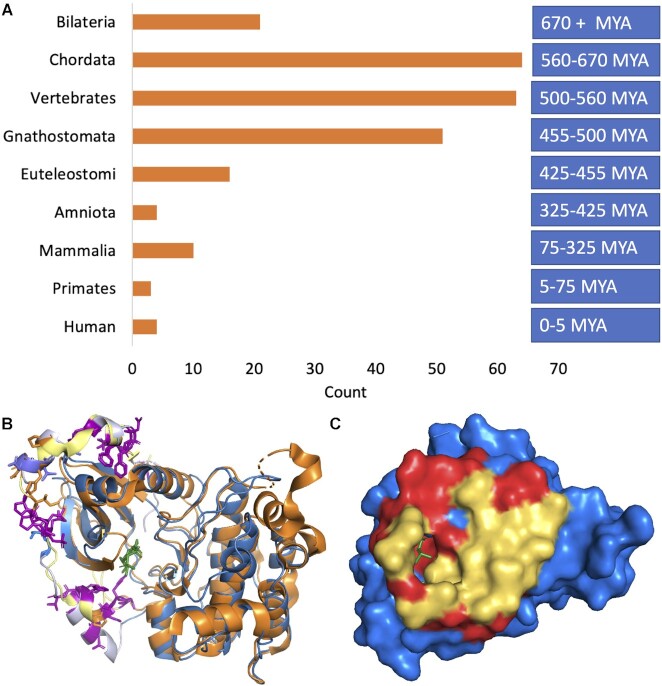
Figure 5.
Age of last common ancestor and two tandem exon substitutions conserved in Bilaterian clade. (A) Last common ancestors of each tandem exon derived duplication event binned by age. Age of the last common ancestor was searched manually using FlyBase, RefSeq and UniProtKB. Approximate ages were estimated from TimeTree (45), see methods section. (B) The tandem exon duplication-derived substitution event in PRKCB mapped onto the structures of Protein kinase C beta (PDB: 3pfq, in blue) and Protein kinase C eta (PDB: 3txo in orange) in cartoon form. The homologous exons code for a C-terminal arm that wraps around the kinase domain. Residues conserved in both exons in vertebrates and invertebrates are shown in stick form in purple and most are hydrophobic residues that anchor the arm to the kinase domain. Residues conserved in one of the two homologous exons and not in the other are shown in stick form in orange and blue. These residues cluster in the helix in the top left-hand corner. (C) The tandem exon duplication-derived substitution event in RAB37 mapped onto the structure of Rab-26 (PDB: 2g6b, blue), showing just the surface of the protein. The residues that are identical in the two homologous regions are shown in red and again are mainly found in the interior. Residues that differ in the homologous region (yellow) form a surface patch that is likely to allow RAB37 isoforms to interact with different proteins.