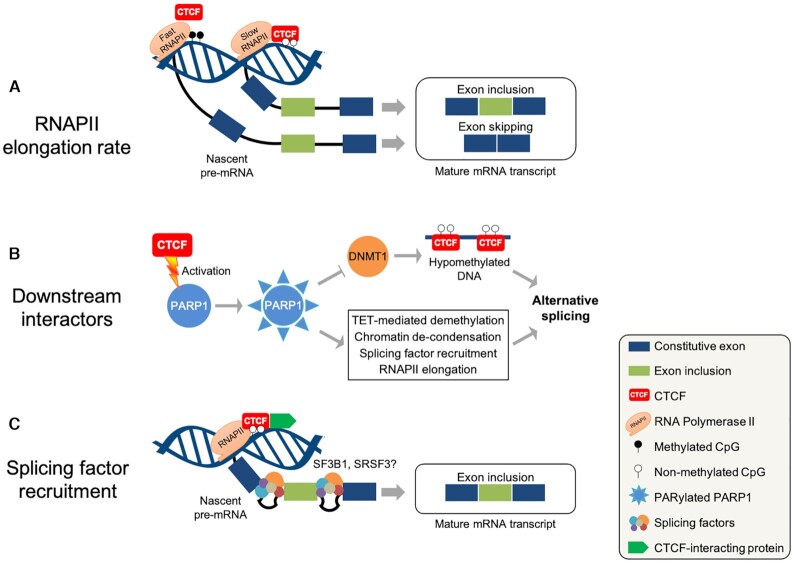
Figure 2.
CTCF-mediated co-transcriptional regulation of alternative splicing. Schematic representation of co-transcriptional mechanisms by which CTCF modulates AS. (A) The ‘roadblock’ mechanism involves altering RNAPII elongation rate in a methylation-dependent manner (33,34). (B) CTCF regulation of DNA methylation via activation of PARP1 and PARylation (60,61), which are also involved in other AS-related regulatory activities (66–69). (C) Splicing factor recruitment might also take part in CTCF-mediated AS regulation through direct interaction with RNA binding proteins (42,58,70) or other transcription factors involved in AS such as PARP1 (66), MeCP2 (38), YB-1 (108,109) and HP1α (46,124,127). SF3B1 and SRSF3 are examples of RNA-binding proteins.