Figure 2.
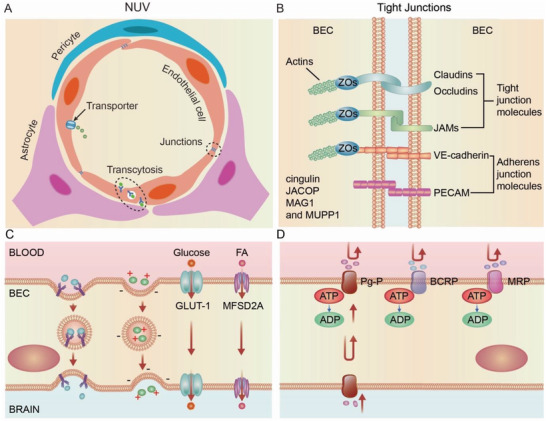
Neurovascular unit (NVU) structure and key features of brain endothelial cells (BECs). A) Cross‐sectional view of the NVU at the level of brain capillaries. Vessels are lined by a single layer of brain endothelial cells surrounded by astrocytes and pericytes. Three key features of brain endothelial cells include specialized tight junctions, low transcytosis, and high efflux transporter, which stringently coordinate and control the exchange of ions and nutrients between the blood and brain. B) Magnified view of the brain endothelial cell specialized tight junctions, which control paracellular permeability. Brain endothelial cells are tightly linked by tight junction molecules, including junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs), occludin, and members of the claudin family. Major adherens junction molecules include VE‐cadherin and PECAM‐1. The cytoplasmic adaptor proteins include zonula occludens (ZOs), cingulin, JACOP, MAG1, and MUPP1 link these transmembrane proteins to the cytoskeleton. C) Brain endothelial cells exhibit low levels of transcellular transport. Receptor‐mediated transcytosis (RMT); Adsorptive‐mediated transcytosis (AMT); Carrier‐mediated transport (CMT). D) Brain endothelial cells express efflux transporters that both shuttle specific nutrients into the brain and remove potentially harmful toxins and other small molecules from the brain, respectively.
