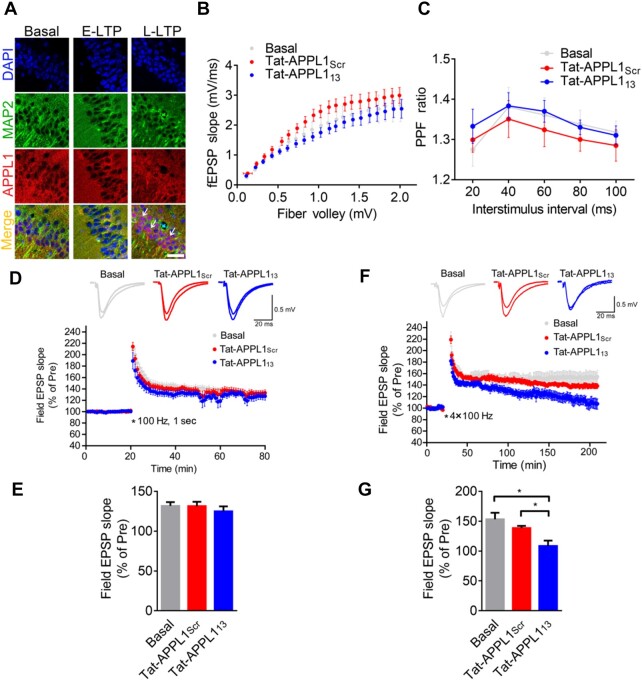
Figure 6.
Retrograde translocation of APPL1-positive TrkB endosomes is required for L-LTP. (A) E-LTP was induced by a single train of 100 Hz in acute hippocampal slices from wild-type mice and L-LTP was induced by four trains of 100 Hz every 3 min and subsequently incubated for 30 min in ACSF at 32°C. Slices were fixed and stained with antibodies against MAP2 (green) and APPL1 (red) and with DAPI nuclear dye (blue). Arrowheads indicate nuclear accumulation of APPL1. Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) The input‒output curve at hippocampal Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses was unchanged when bath-applied with Tat-APPL113 (n = 6 slices, 4 mice) compared to untreated (basal, n = 5 slices, 3 mice) or treated with Tat-APPL1Scr (n = 6 slices, 4 mice). (C) The paired-pulse ratio was unchanged when bath-applied with Tat-APPL113 (n = 5 slices, 3 mice) compared to untreated (basal, n = 5 slices, 3 mice) or treated with Tat-APPL1Scr (n = 5 slices, 3 mice). (D and E) E-LTP was induced by one train of 100-Hz simulation (100 Hz, 1 sec). Perfusion with Tat-APPL113 has no effect on the maintenance (last 10 min, n = 7 slices, 4 mice) of E-LTP compared to the basal group (n = 9 slices, 5 mice) or Tat-APPL1Scr group (n = 9 slice, 5 mice). Scale bars, 20 ms, 0.5 mV. (F and G) L-LTP was induced by four trains of tetanic stimulation (3 min apart). Perfusion with Tat-APPL113 significantly decreased the maintenance of L-LTP (n = 8 slices, 8 mice) compared to basal group (n = 7 slices, 7 mice), while perfusion with Tat-APPL1Scr (n = 6 slices, 6 mice) showed no effect (last 10 min). Sample traces 10 min before and 1 or 3 h after the tetanus. Scale bars, 20 ms, 0.5 mV. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.