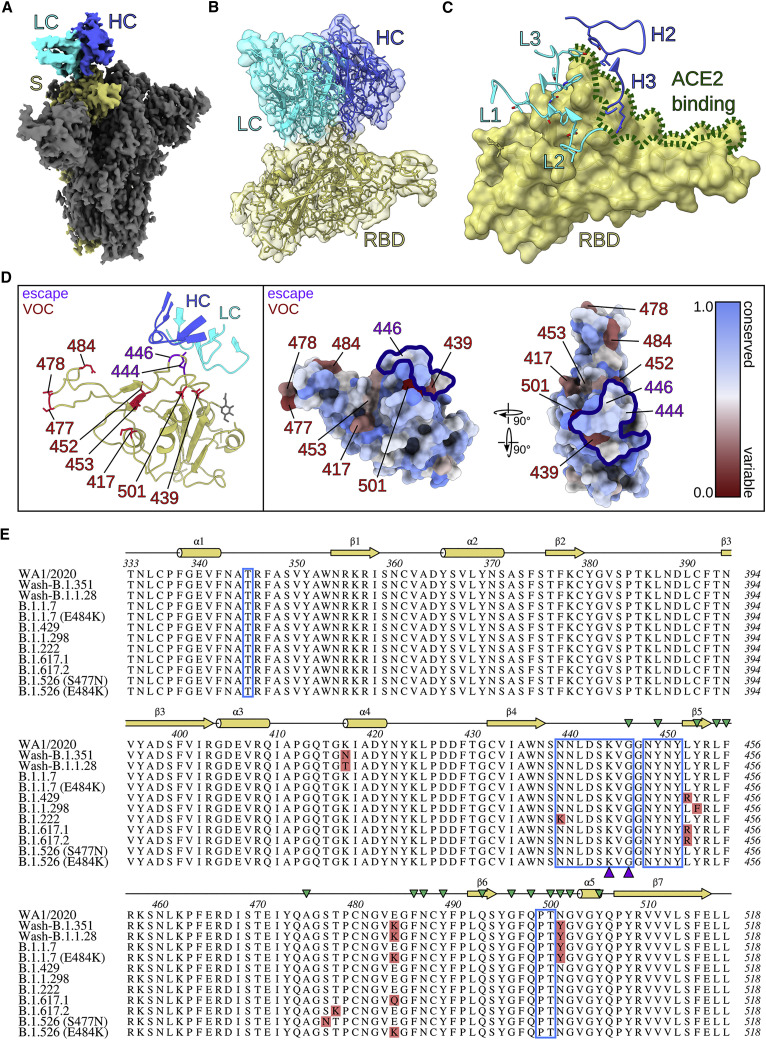
Figure 6.
SARS2-38 targets a conserved portion of the RBM with extensive light chain contact
(A) Density map of SARS2-38 Fv bound to trimeric SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with all RBDs in the down position. The spike monomer bound by SARS2-38 is shown in yellow, with the rest of the trimer colored gray. The SARS2-38 heavy chain is shown in royal blue and the light chain in cyan.
(B) Focused density map of the Fv/RBD complex encompassing a refined atomic model. The RBD is shown in yellow. The SARS2-38 heavy and light chains are colored royal blue and cyan, respectively.
(C) Complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) of SARS2-38 overlay a surface rendering of the RBD. CDRs from the heavy and light chains are colored royal blue and cyan, respectively, with the RBD colored yellow. ACE2-binding residues of the receptor binding motif (RBM) are outlined in green.
(D) Left panel: a ribbon diagram of the RBD and SARS2-38 CDRs, with escape mutations and variants of concern (VOC) noted in purple and red, respectively. The RBD is otherwise colored yellow, with a gray glycan linked to N343. CDRs of the SARS2-38 heavy and light chains are colored royal blue and cyan, respectively. Right panel: surface renderings of RBD colored according to conservation of surface residues (blue = conserved, red = variable). Escape mutations and VOCs are noted in purple and red, respectively. The SARS2-38 epitope as determined by protein interfaces, surfaces, and assemblies (PISA) solvent exclusion analysis is outlined in navy.
(E) Multiple sequence alignment of RBD (residues 333–518) from WA1/2020 and SARS-CoV-2 VOC, with the PISA binding footprint of SARS2-38 boxed in blue. Mutations within SARS-CoV-2 VOC are highlighted in red, and SARS2-38 escape mutation contacts are marked with purple triangles. Secondary structure annotation is displayed above the alignment in yellow, with ACE2 contacts designated by green triangles (Lan et al., 2020).