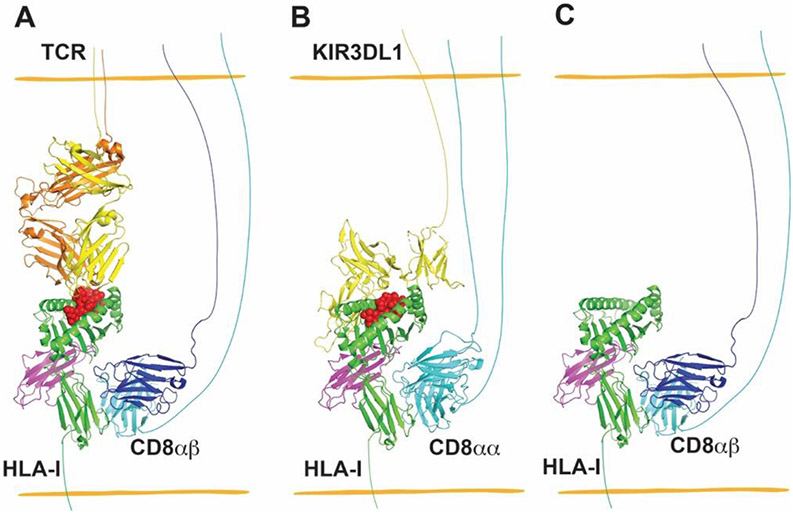
Figure 3.
Interactions between MHC-I and CD8 provide co-receptor-based synergy for receptors of CD8+ T cells and NK cells (A and B), and enhanced binding between CD8 and peptide-free versions of some MHC-I allotypes contributes to increased adhesion between CD8-expressing cells and MHC-I-expressing target cells (C). (A) CD8αβ heterodimers are co-receptors for TCR recognizing cognate pHLA-I. The structure of TCR–HLA-A*02:01 complex (PDB: 5c0a) was superimposed with H2-Dd- CD8αβ (PDB: 3dmm) by aligning HLA-A*02:01 and H2-Dd, and H2-Dd was then deleted to generate a model for the TCR–HLA-A*02:01-CD8αβ complex. (B) A model for the complex between CD8αα and KIR3DL1 of NK cells with HLA-I of target cells, wherein CD8αα has co-receptor function in NK cells, similar to that for CD8αβ in T cells. The structure of KIR3DL1–HLA-B*57:01 complex (PDB: 3vh8) was superimposed onto HLA-A*02:01-CD8αα (PDB: 1akj) by aligning HLA-B*57:01 and HLA-A*02:01, followed by deletion of HLA-A*02:01 to generate a model for the KIR3DL1-HLA-B*57:01-CD8αα complex. (C) CD8 has been shown to preferentially bind to the empty version of HLA-B*35:01 relative to specific peptide-filled versions. To depict this type of interaction, peptide was deleted from the structure of H2-Dd-CD8αβ (PDB: 3dmm) to model a peptide-free MHC-I allotype binding to CD8αβ of CD8+ T cells. PyMOL was used to visualize the structures of HLA-I and its receptors.