Figure 1.
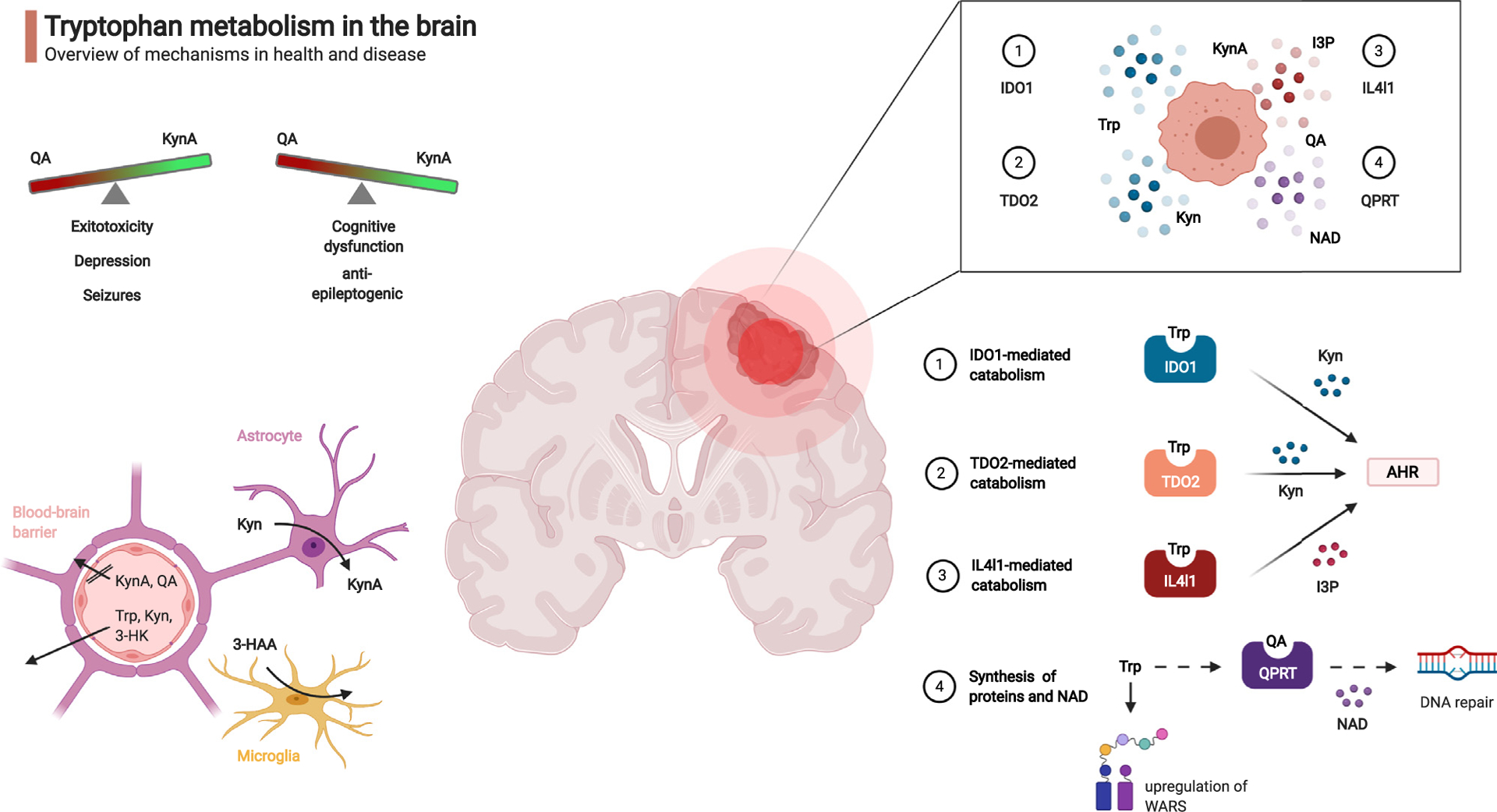
Tryptophan metabolism in the brain.
Tryptophan (Trp) catabolites regulate neurological and immunological functions in health and disease. Top left: overview of neuropsychiatric effects of Trp catabolites. Bottom left: Blood-brain barrier and glial cells determine local transport and metabolism of Trp and Trp-catabolites. Top right: Pleiotropic enzymatic digestion of exogenous Trp by brain tumor cells. Bottom right: Mechanisms for enzymatic digestion of Trp and biological effects of downstream catabolites. Kyn: kynurenine, KynA: kynurenic acid, QA: quinolinic acid, 3-HAA: 3-hydroxy-anthranilic acid, 3-HK: 3-hydroxykynurenine, IDO1: indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase, IL4I1: Interleukin-4-Induced-1, I3P: indole-3-pyruvic acid, TDO2: tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase, QPRT: quinolinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase, AHR: aryl hydrocarbon receptor, NAD: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, WARS: tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase.
