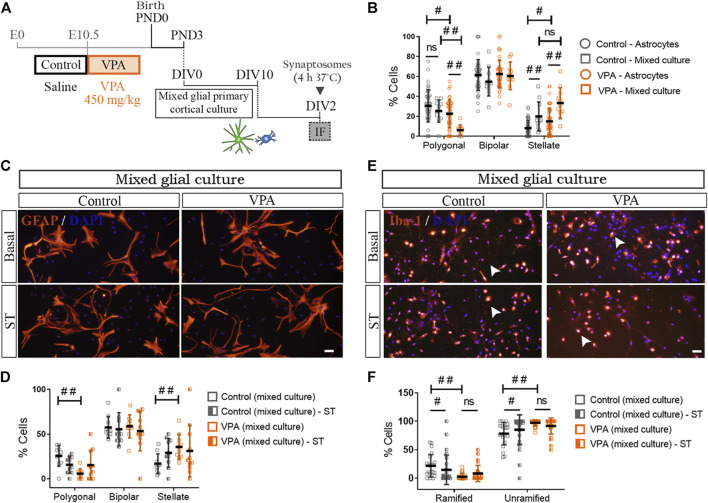
FIGURE 6.
Impact of astrocyte-microglia crosstalk on morphological profiles and responses to synaptic terminals of glial cells isolated from control and VPA animals. (A) Mixed cortical glial cultures isolated from control and VPA animals were exposed to synaptosomes (ST) (DIV2). (B) In mixed glial cultures from control animals, the presence of microglia increased the proportion of stellate astrocytes compared with astroglial-enriched cultures (astrocytes). In the VPA group, the presence of microglia increased stellate and decreased polygonal astrocytes when compared with astroglial-enriched cultures (astrocytes). (C) Mixed glial cultures from control and VPA animals under basal conditions and after exposure to cortical ST immunostained for GFAP and labeled with DAPI. (D) In mixed glial cultures, astrocyte morphology is not altered by exposure to ST in either control or VPA group. (E) Mixed glial cultures from control and VPA animals immunostained for Iba1 and labeled with DAPI under basal conditions and after exposure to cortical ST. (F) While in mixed glial cultures from control animals exposed to ST, microglia responded with a decrease in ramified cells and an increase in unramified cells, in mixed cultures isolated from VPA animals, microglia failed to respond. Results are expressed as mean values (±SD) (B): 11 photomicrographs per group from two independent mixed cultures and 47 photomicrographs per group from three independent astroglial-enriched cultures. (D,F) 10–26 photomicrographs per group from 2 independent mixed cultures; ns: non-significant; #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01 between groups by Kruskal–Wallis test. Scale bars: 50 µm.