Figure 2.
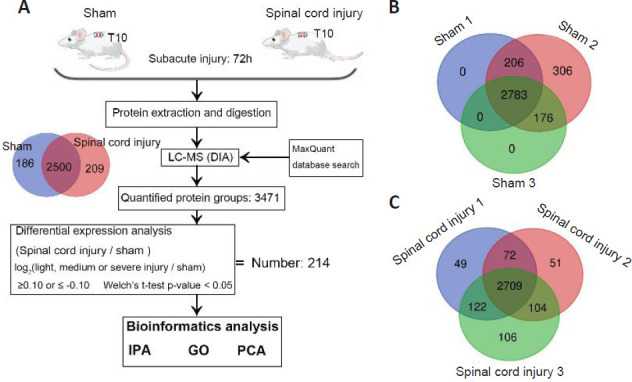
Proteomic identification of proteins associated with spinal cord injury.
(A) An LC-MS approach was used to analyze spinal cord sections from sham and spinal cord injury model rats (n = 3/group) at 72 hours post-injury. In total, 3471 proteins were identified in these two groups, including 2500 that overlapped between both sample types. In total, we identified 214 differentially expressed proteins associated with spinal cord injury, after which IPA, GO, and PCA were used to functionally analyze these proteins. (B, C) Venn diagrams of the protein numbers in sham (B) and spinal cord injury (C) groups. In total, 3471 proteins were detected in sham samples, including 2783 that were detected in all three samples. In total, 3213 proteins were detected in spinal cord injury samples, including 2709 that were detected in all three samples. These analyses were repeated three times. DIA: Data independent acquisition; GO: gene ontology; IPA: ingenuity pathway analysis; LC-MS: liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; PCA: principal component analysis.
