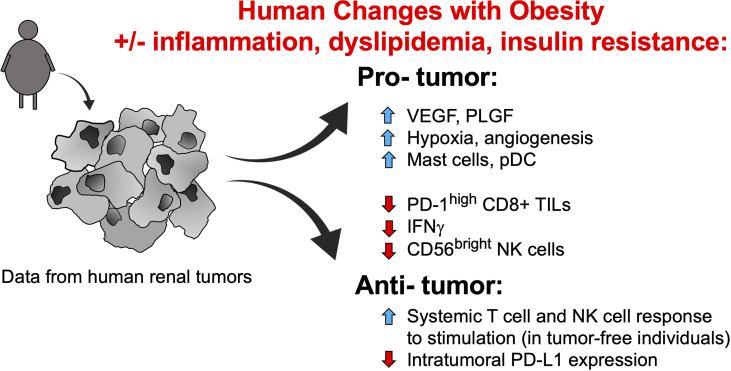
Figure 2.
Identified obesity-associated changes in humans that are predicted to facilitate renal tumor progression. Studies of tumor-free individuals and human renal tumors suggest that many obesity-associated changes to the immune compartment and soluble growth factors should favor tumor progression, although some alterations that would promote enhanced tumor clearance and/or ICI efficacy have also been noted. Note that the contributions of obesity-associated factors such as inflammation, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance remain unclear, in terms of their combined effects on immune function. NK, natural killer; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; pDCs, plasmacytoid dendritic cells; PLGF, placental growth factor; TILs, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.